Figure 2. LB100 enhances radiation sensitivity.
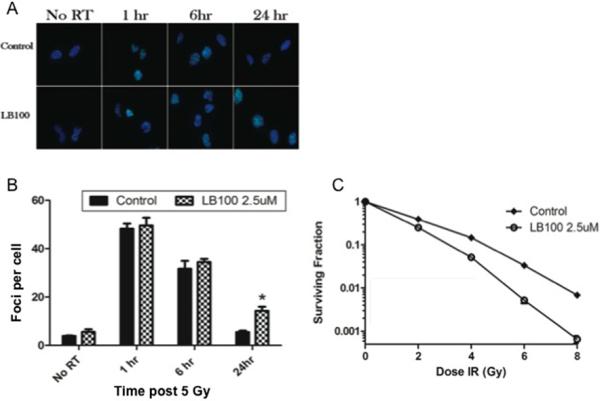
(A) Immunocytochemical staining to detect γ-H2AX foci was performed. Cells were plated in 4 well chamber slides, allowed to attach (6 hours) and then incubated in LB100 (2.5 μM) for 4 hours prior to radiation (5 Gy). Foci were counted in at least 50 cells per experiment. (B) Quantitative assessment of γ-H2AX foci per cell at 1 hour, 6 hours, and 24 hours after radiation is shown. Data presented are the mean ± SE from at least three independent experiments. *, P < 0.05 (comparing both radiation alone and LB100 alone treated cells to the combination treatment). (C) The effects of LB100 on radiosensitivity of U251 are demonstrated by clonogenic assay. Cells were seeded as a single-cell suspension with a specified number of cells. After allowing cells time to attach (6 hours), 2.5 μM LB100 was added and the plates were radiated 4 hours later and drug removed after 24 hours. Twelve days after seeding, survival curves were generated after normalizing for the cytotoxicity generated by LB100 alone. Plating efficiency was 0.31 and treatment with LB100 yielded a surviving fraction of 0.68. The addition of LB100 to radiation resulted in a dose enhancement factor of 1.45 at a surviving fraction of 0.10.
