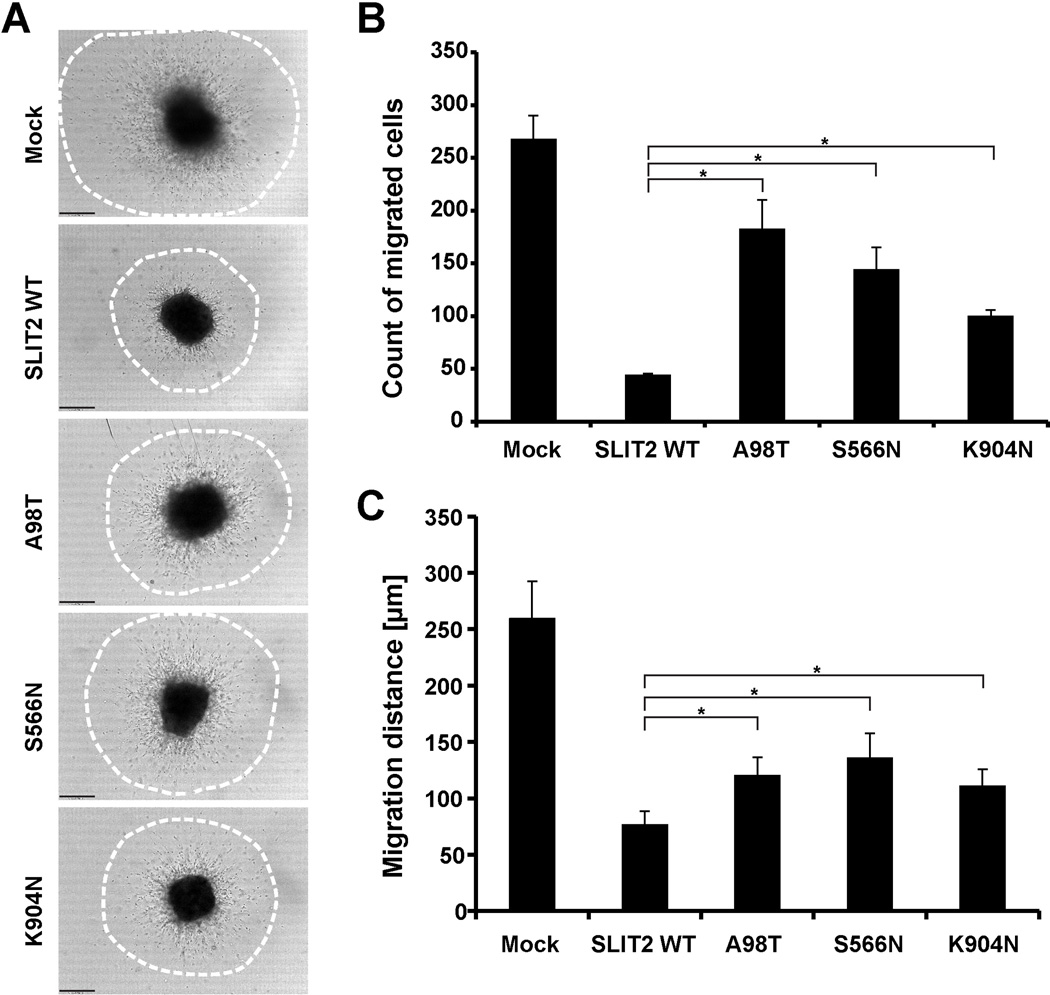
Figure 4. SLIT2 mutations identified in CAKUT patients compromise its inhibition of SVZa neuronal migration.
(A) Representative DIC images show SVZa neuronal migration after 24 hours in the presence of SLIT2 wild-type (WT) or SLIT2 mutants (A98T, S566N, K904N) conditioned media. Media from mock transfected HEK293T cells were used as a negative control. Note that wild-type SLIT2 inhibits neuronal migration whereas the SLIT2 mutants show a diminished inhibition. Dot circles in processed image column represent the areas where the number of migrated cells out of SVZa explants and migration distance were quantified (see also Supplementary Figure 6 online).
(B) Quantification of migrated SVZa cell counts in (A). Note wild-type SLIT2 has less migrated cells out of SVZa explants. SLIT2 mutants A98T, S566N, and K904N show a diminished inhibitory effect on migrated cell counts.
(C) Quantification of average SVZa cell migration distances in (A). Note wild-type SLIT2 inhibits migration of SVZa cells. SLIT2 mutants A98T, S566N, and K904N show a reduced inhibitory effect on migration indicating partial loss-of-function.
Scale bar: 100µm.
*, P< 0.05 (Student’s t-test); Error bars indicate one standard deviation (n=3).