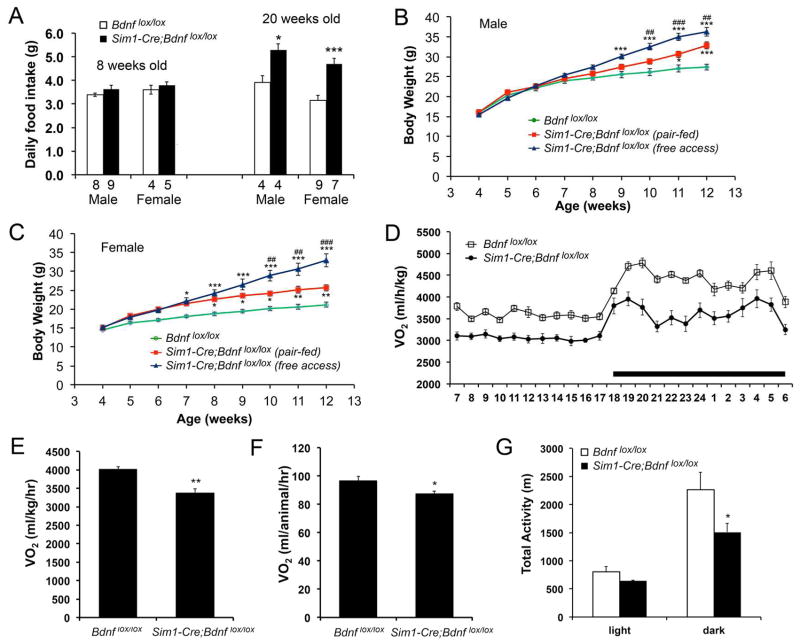
Figure 3. Reduced energy expenditure in Sim1-Cre;Bdnflox/lox mice.
(A) Daily food intake at 8 and 20 weeks of age. The numbers of mice used are indicated under each column.
(B) Body weight of male Sim1-Cre;Bdnflox/lox mice with free access to food or fed with the amount of food ingested by male Bdnflox/lox mice. Two-way ANOVA for the effect of treatment on body weight: F(2, 198) = 57.22 (n=7–10 mice per group), P < 0.001. * P < 0.05 and *** P < 0.001 when compared to Bdnflox/lox mice using Bonferroni post-hoc test. ## P < 0.01 and ### P < 0.001 when mutant mice with free access to food were compared to pair-fed mutant mice using Bonferroni post-hoc test.
(C) Body weight of female Sim1-Cre;Bdnflox/lox mice with free access to food or fed with the amount of food ingested by female Bdnflox/lox mice. Two-way ANOVA for the effect of treatment on body weight: F(2, 198) = 102.12 (n=6–11 mice per group), P < 0.001. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, and *** P < 0.001 when compared to Bdnflox/lox mice using Bonferroni post-hoc test. ## P < 0.01 and ### P < 0.001 when mutant mice with free access to food were compared to pair-fed mutant mice using Bonferroni post-hoc test.
(D) Distribution of VO2 over a 24-hr period in male mice at 8 weeks of age. The body weights of the mice were 24.0 ± 0.5 g for Bdnflox/lox and 26.1 ± 1.3 g for Sim1-Cre;Bdnflox/lox (P = 0.143). Two-way ANOVA for the effect of genotype: F(1, 216) = 359.74 (n=5–6 per genotype), P < 0.001.
(E–G) Oxygen consumption and locomotor activity of male Bdnflox/lox and Sim1-Cre;Bdnflox/lox mice at 8 weeks of age (n=5–6 mice per genotype).
Error bars indicate standard errors.