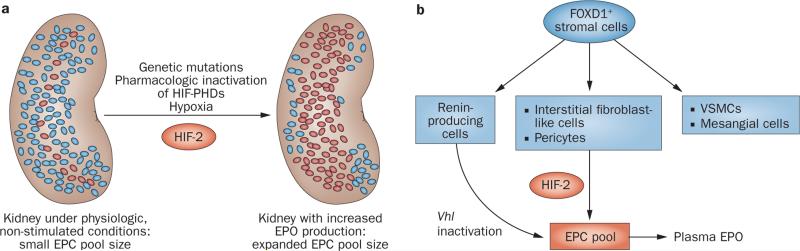
Figure 4.
The number of EPCs regulates renal erythropoietin output. a | Under physiologic, non-stimulated conditions a small number of renal EPCs are responsible for renal erythropoietin output. The size of the EPC pool is regulated in an oxygen-dependent manner and increases under hypoxic conditions. The expansion of the EPC pool requires HIF-2 signalling, which is activated by hypoxia, pharmacologic PHD inhibition, or as a consequence of mutations in the oxygen-sensing pathway. b | Renal EPCs are derived from FOXD1-expressing stromal cells, and include interstitial fibroblast-like cells, pericytes and renin-producing cells. Renin-producing cells can be induced to synthesize erythropoietin under conditions of Vhl gene inactivation; their role in hypoxia-induced renal erythropoietin production is unclear. Abbreviations: EPC, erythropoietin-producing cell; EPO, erythropoietin; HIF-2, hypoxia-inducible factor-2; VSMC, vascular smooth muscle cell.