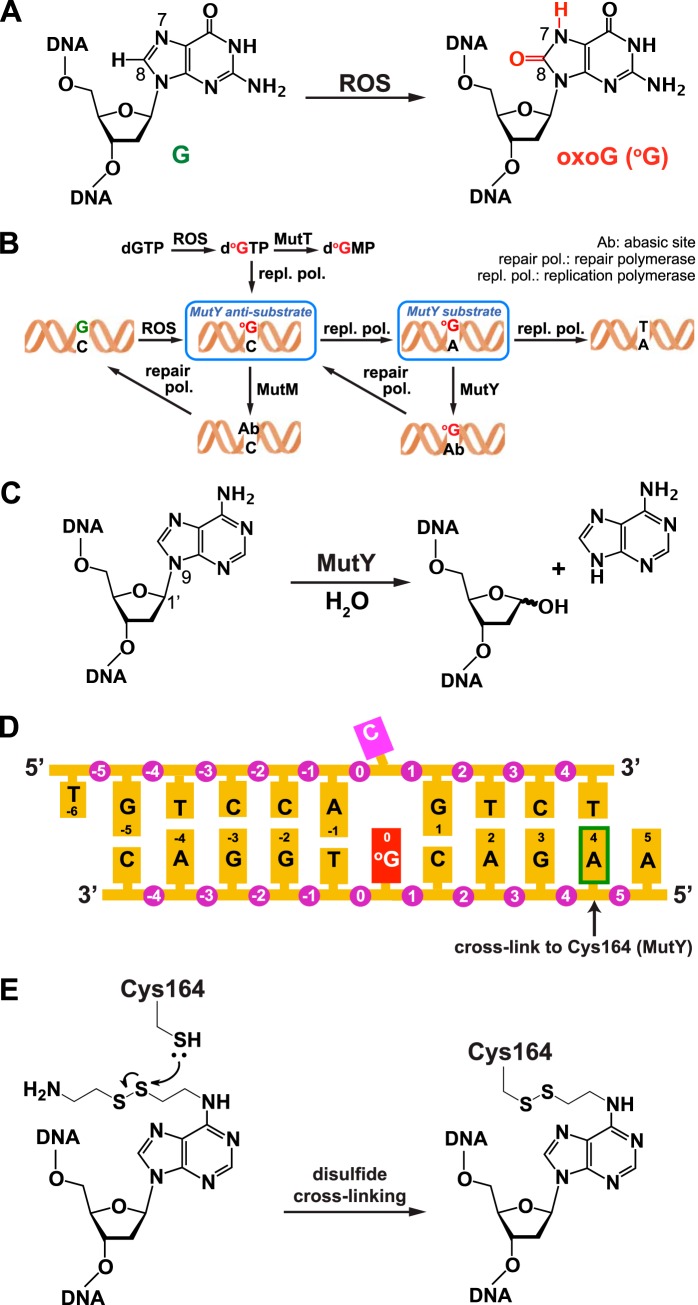
FIGURE 1.
Generation and repair of oxoG:C and oxoG:A lesions in DNA. A, the primary oxoG lesion is formed by attack of reactive oxygen species (ROS) on a guanine residue. B, pathway for repair of oxoG lesions in DNA. C, hydrolytic cleavage of the target glycosidic bond catalyzed by MutY. D, duplex DNA sequence used in this work. The arrow indicates the adenine that is modified (as shown in panel E) to cross-link to an engineered Cys residue in MutY. E, structure of the modified adenine used in disulfide cross-linking and of the covalent linkage it forms with MutY.