FIGURE 1.
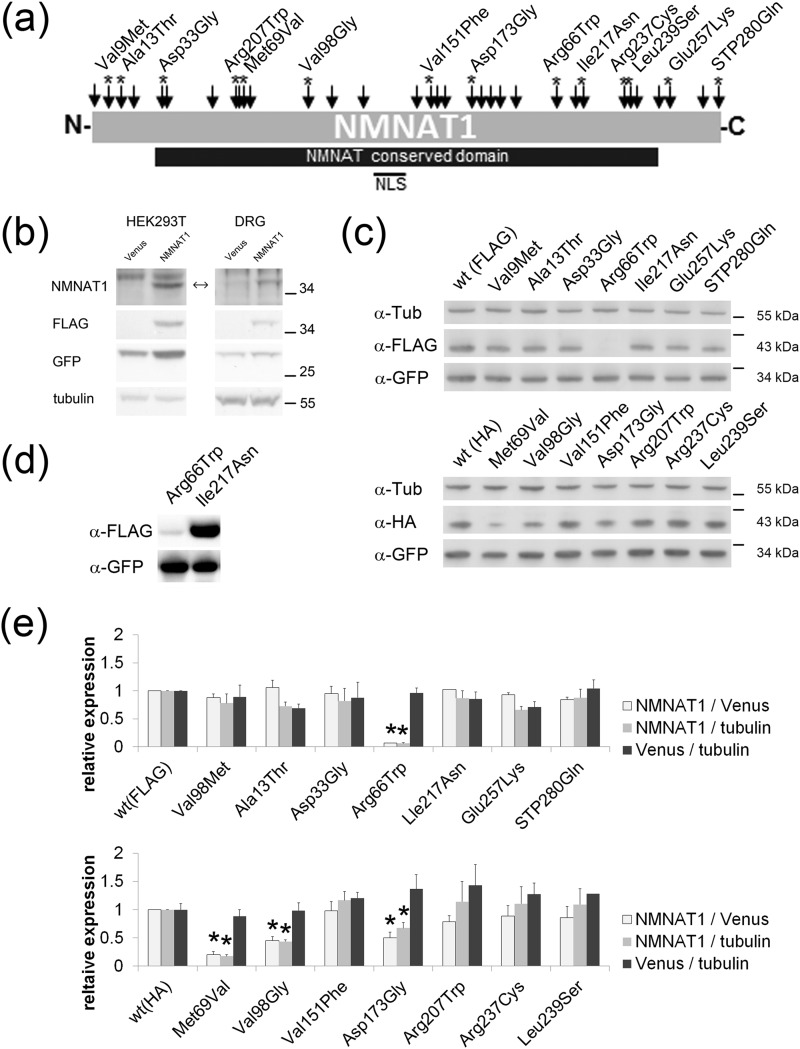
NMNAT enzymatic activity of LCA-associated NMNAT1 mutants. a, schematic displaying locations of LCA-associated mutations in NMNAT1 (arrows). Asterisks indicate mutations analyzed in this study. b, lysates from HEK293T cells (left column) or DRG neurons (right column) expressing Venus or FLAG-tagged wild type NMNAT1 (left column) were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to NMNAT1, FLAG, GFP, or α-tubulin. Note that endogenous NMNAT1 levels are undetectable with this antibody in both HEK293T cells and DRG neurons. c, lysates from HEK293T cells expressing FLAG- or HA-tagged wild type or mutant NMNAT1 from the FCIV expression construct containing an IRES-Venus cassette were analyzed by Western blotting using antibodies to FLAG, HA, or GFP. Note that expression of R66W and M69V mutants was significantly lower than other NMNAT1 proteins. Venus expression serves as transfection control. d, longer exposure of Western blot of R66W and I217N NMNAT1 mutants shows proteins of normal size but very low expression in case of R66W. e, quantification of protein expression of NMNAT1 (FLAG- or HA-tagged), Venus, and α-tubulin (endogenous marker) in HEK293T cells. The ratio of NMNAT1 to Venus, NMNAT1 to α-tubulin, or Venus to α-tubulin are shown for each NMNAT1 mutant. The values were normalized to the corresponding either FLAG- or HA-tagged wild type NMNAT1. Asterisks denote significant reduction of NMNAT1 expression compared with wild type NMNAT1 (p < 0.005 t test).