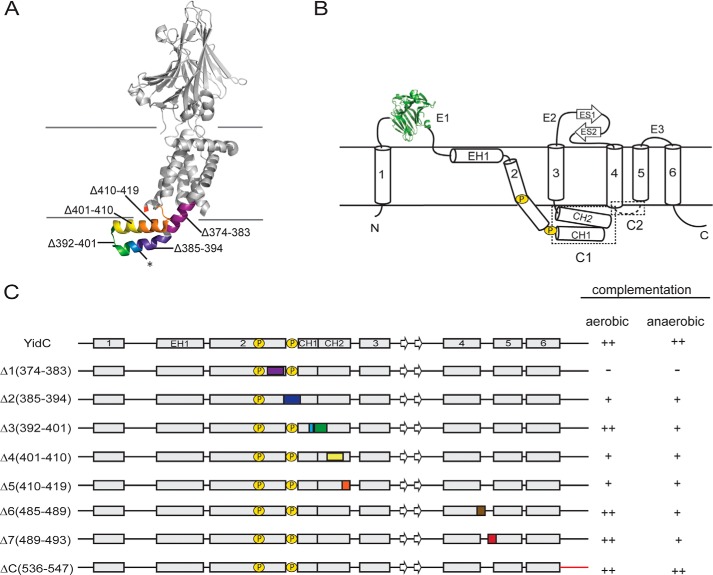
FIGURE 1.
Overview of E. coli YidC variants. A, a ribbon representation of the E. coli YidC structure. The short regions of E. coli YidC that were deleted are colored in the range of purple to red from the N terminus to the C terminus. The cytosolic loop C2 and the C terminus are structurally disordered. B, a topology diagram of E. coli YidC. Helices and strands are indicated by cylinders and arrows, respectively. The CH1 and CH2 helices in the cytosolic loop C1 fold into a hairpin-like structure. The cytoplasmic loops C1 and C2 are highlighted in the dashed boxes. C, a schematic representation of designed E. coli YidC variants. The numbers in parentheses indicate the positions of amino acid residues in E. coli YidC, and the deletion fragments are colored as in A. The prolines in TM2 are indicated by a circled P. Because of the structural disorder of cytosolic loop C2 and the C terminus in E. coli YidC, the YidCΔ6, YidCΔ7, and YidCΔC variants are not shown in A. In addition, a summary of the growth complementation by the variants is indicated for FTL10 cells grown under aerobic and anaerobic conditions as described under “Experimental Procedures” and in the legend of Fig. 2.