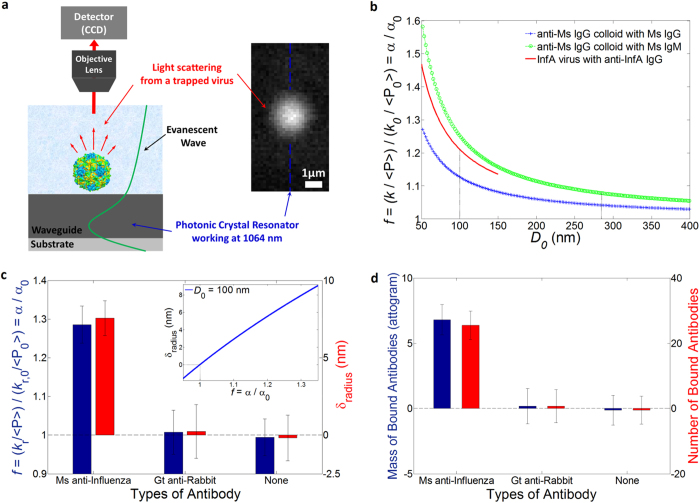
Figure 5. Binding of antibodies to a human influenza A H1N1 virus (Dmean ≈ 100 nm).
(a) Experimental setup of the light scattering imaging. The inset shows a trapped virus particle (Dvirus ≈ 100 nm). (b) Analytical plot of predicted relative power-normalized trap stiffness Note that variables including f and kr are defined same as explained in a main text. (c) Measured relative power-normalized trap stiffness and radius increases for different solutions of mouse anti-influenza IgG (N = 3) and goat anti-rabbit IgG (N = 3), and a buffer (N = 3). N represents a number of independently performed experiments. The inset shows an analytical plot of the radius change to the relative polarizability for an influenza virus with D0 = 100 nm. (d) Stoichiometry of the antibodies to the influenza virus. All error bars are determined by (∑σf2)1/2/N (see SI for details on σf).