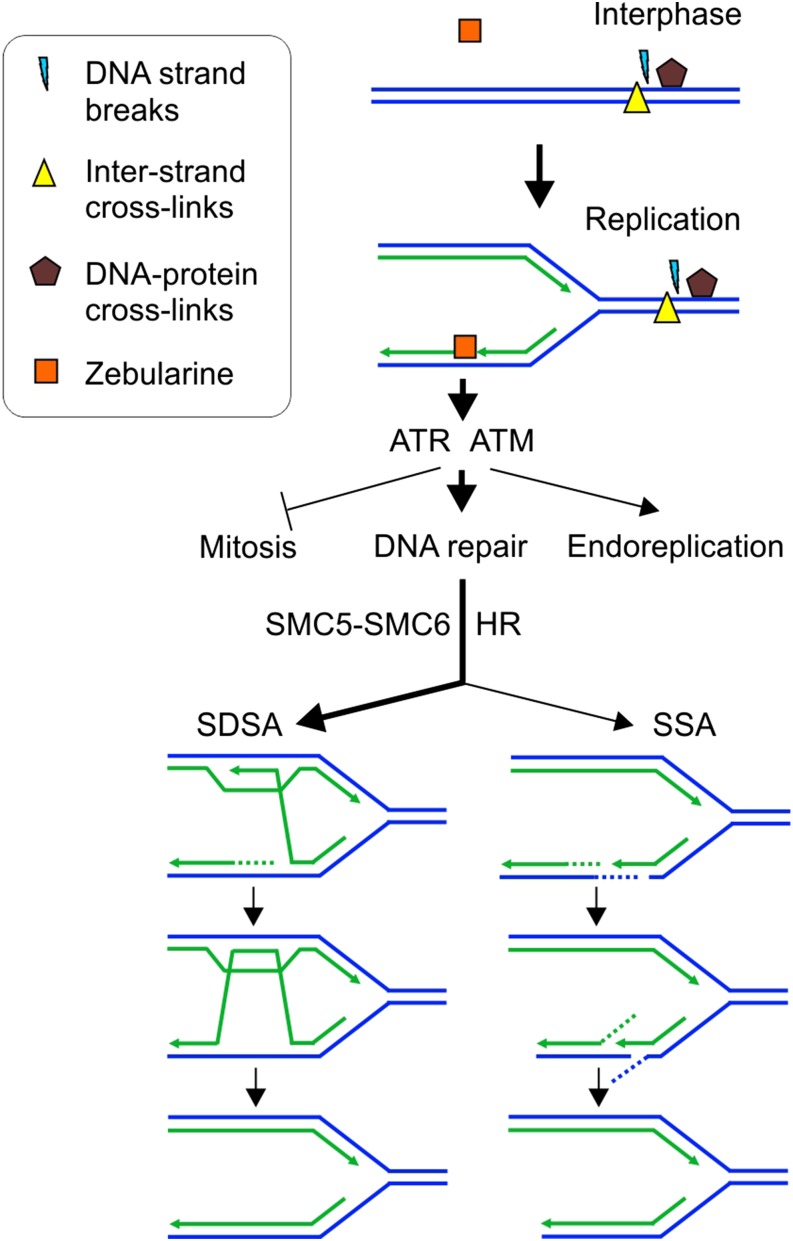
Figure 6.
The Model of Zebularine-Induced Damage and Its Repair.
Most types of DNA damage, including DNA-protein cross-links, DNA strand breaks, or interstrand cross-links, can occur irrespectively of the cell cycle phase. In contrast, zebularine damage occurs during DNA replication in course of new DNA strand synthesis. This causes DNA damage stress, which suppresses cell division, promotes endoreplication, and activates DNA damage repair signaling by ATR and ATM activity. The repair depends strongly on SMC5-SMC6 activity and is pursued primarily by SDSA and to a smaller extent also SSA homologous recombination pathways.