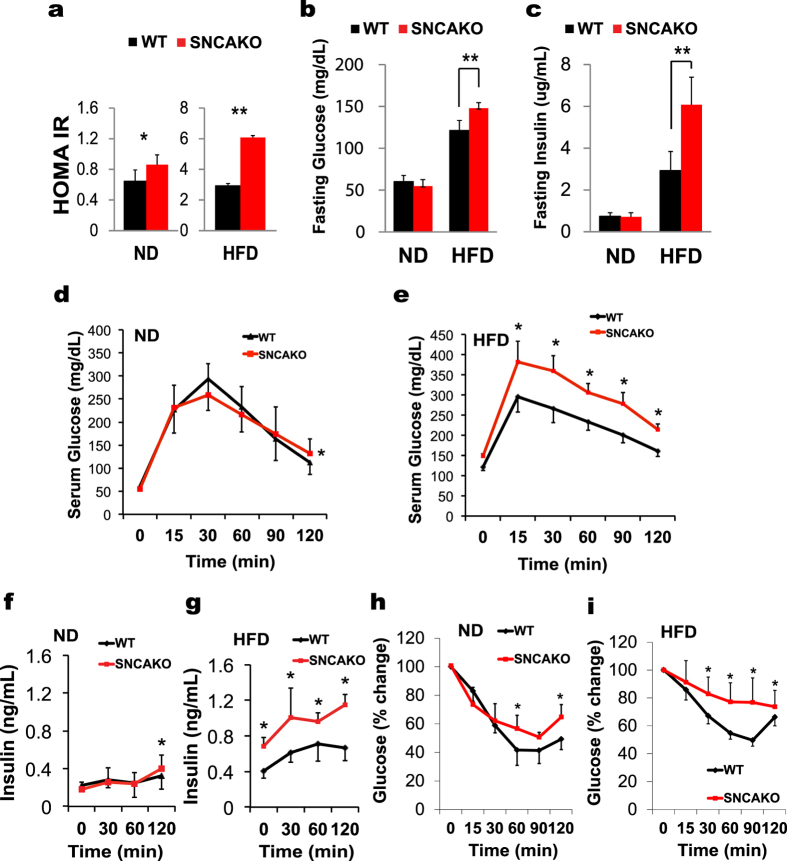
Figure 1. SNCAKO mice display disturbances in glucose metabolism.
(a) Homeostatic model assessment index for insulin resistance (HOMA IR) in WT and SNCAKO mice after 5 weeks of a HFD. n = 10, each group. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 via ANOVA. (b) Fasting blood glucose measurements in WT and SNCAKO mice fed a normal diet (ND) and a high-fat diet (HFD) for 5 weeks. n = 10, each group. (c) Fasting immunoreactive insulin measurements in WT and SNCAKO mice fed a ND or a HFD for 5 weeks. n = 10, each group. (d) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (ipGTT, 2 g/kg) after 5 weeks of a ND in the WT and SNCAKO mice. n = 10, each group. (e) Intraperitoneal glucose tolerance test (ipGTT, 2 g/kg) after 5 weeks of a HFD in the WT and SNCAKO mice. n = 10, each group. (f) Serum insulin measurement (ELISA) during ipGTT in WT and SNCAKO mice fed a ND at 0, 30, 60 and 120 min. n = 10, each group.(g) Serum insulin measurement (ELISA) during ipGTT in WT and SNCAKO mice fed a HFD at 0, 30, 60 and 120 min. n = 10, each group. (h) Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (ipITT, 0.8 IU/kg) under a ND. n = 10, each group. (i) Intraperitoneal insulin tolerance test (ipITT, 0.8 IU/kg) after 5 weeks of a HFD. n = 10, each group. From (b) to (i): P < 0.05 was obtained for the area under the curve comparisons between the SNCAKO and WT groups (ANOVA test). In all the experiments: *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01.All histogram bars show the means ± s.d.