Figure 3.
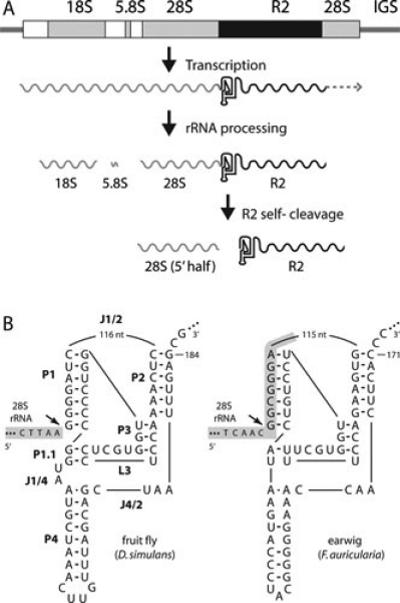
The R2 ribozyme. (A) An rDNA transcription unit is diagramed with 18S, 5.8S, and 28.S genes (gray boxes), transcribed spacers (white boxes), and R2 insertion (black box). All three rRNAs are normally processed from the single primary transcript. When a unit contains an R2 insertion, a self-cleaving ribozyme encoded at the 5’ end of the element releases the 5’ end of the R2 transcript from the upstream 28S rRNA sequence. It is not known if transcription ends at the 3’ end of the R2 element, or if this end is processed from downstream 28S gene sequences. (B) On the left is the D. simulans R2 ribozyme folded in a structure similar to that of the hepatitis delta virus (HDV) ribozyme (80,81). The various components of the ribozyme are labeled as in the HDV ribozyme: P, base-paired region; L, loop; J, nucleotides joining paired regions. 28S gene sequences are shaded with gray. On the right is the R2 ribozyme from Forficula auricularia (earwig). Self-cleavage (arrow) occurs at the precise junction of the R2 element with the 28S gene in the case of the D. simulans element and upstream of the junction in the 28S gene sequences in the case of the R2 element from F. auricularia.
