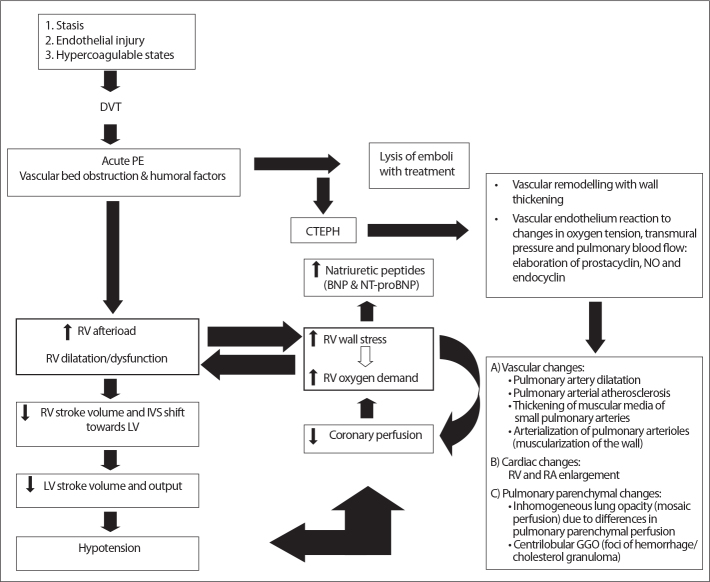
Figure 2.
Pathophysiology of hemodynamic instability due to pulmonary embolism, development of CTEPH, and its cardiovascular and pulmonary parenchymal changes. Predisposing factors may cause DVT that can dislodge and cause pulmonary embolism. Pulmonary embolism can cause RV failure directly or indirectly after inadequate lysis of emboli and development of CTEPH. Right lower box shows morphologic changes that may be observed on CT. DVT, deep vein thrombosis; PE, pulmonary embolism; RV, right ventricular; LV, left ventricular; IVS, interventricular septal; CTEPH, chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension; BNP, brain natriuretic peptide; NT-proBNP, aminoterminal-probrain natriuretic peptide; NO, nitric oxide; RA, right atrial; GGO, ground glass opacity.