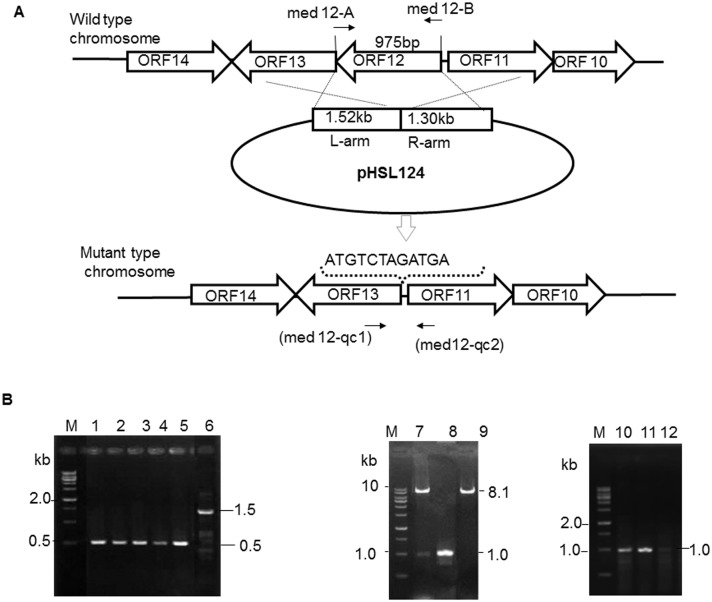
Fig 4. Inactivation and complementation of med-ORF12.
A: Schematic representation of knock-out med-ORF12. A 2.8 kb genomic fragment is composed of left arm (L-arm) and right arm (R-arm) referring to the upstream and downstream regions flanking med-ORF12 respectively. These two DNA regions are linked together and then inserted into a suicide vector pYH7, giving a suicide plasmid pHSL124. After double- crossover between chromosome of the wild type strain and homologous regions on pHSL124, med-ORF12-deficient mutant strain was acquired. On the chromosome of the mutant, an artificially-designed sequence (ATG TCTAGA TGA) containing XbaI site in underline and start codon/stop codon in bold to replace in-frame med-ORF12 in the full-length. B: PCR confirmation of med-ORF12-deficient mutant strain (MS) and complementary strain (CS). The amplification using wild-type strain genomic DNA (lane 6) as template and a primer set (med12-qc1/ med12-qc1, showed in arrow in A) produced a 1 488 bp PCR product, while the genomic DNA of the med-ORF12- deficient mutant strains (lane 1–5) gave a 513 bp band as expected. The 975 bp genomic fragment of med-ORF12 was amplified by PCR (lane 8) and inserted into an integrative vector pIJ8600 (8.1 kb, lane 9: digestion with NdeI and BamHI), generating an expression plasmid pHSAYT19 (lane 7: double digestion with NdeI and BamHI). Genomic DNA isolated from the complementary strains (lane 10) and a primer set (med 12-A/med 12-B shown in arrow in A) were used for PCR amplification, giving a 975 bp band indicating the presence of med-ORF12, as same as for wild type strain genomic DNA as template (lane 11). On the contrary, the med-ORF12-deficient mutant strain (lane 12) could not produce an expected a 975 bp PCR product. M is 1 kb ladder as DNA marker.