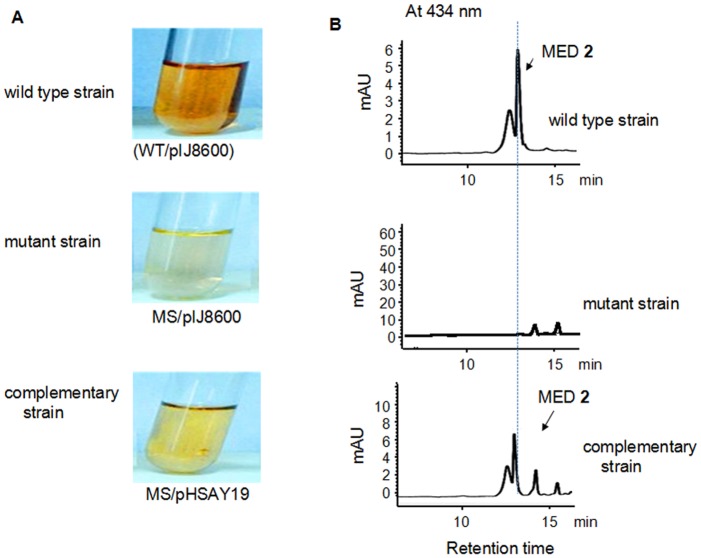
Fig 5. Metabolite analysis of Streptomyces strains.
A: Comparison of the pigmentation in liquid cultures between medermycin-producing wild type strain (WT) and its derived strains. Red-brown pigmentation acts as indicator for MED 2 production. The mutant strain (MS) was a med-ORF12 deficient strain. The complementary strain was obtained by transforming the expression plasmid pHSAY19, derived from pIJ8600, into med-ORF12 deficient mutant strain. Expression of med-ORF12 on pHSAY19 in the complementary strain was induced by thiostrepton (12.5 mg/ml). The wild type and mutant strains were transformed with the vector pIJ8600. B: HPLC spectra of metabolites in wild type, mutant and complementary strains, indicated as UV absorption at 434 nm of crude extracts of Streptomyces strains in A. In a contrast to wild type strain (WT/pIJ8600), the mutant strain (MS/pIJ8600) could not produce MED 2 due to the deficiency of med-ORF12. The reintroduction of med-ORF12 could restore the production of MED 2 in the complementary strain in a comparable yield to that in the wild type strain.