Figure 1. Odds of low Nt-proBNP levels in black compared with white participants in the Dallas Heart Study, overall and in selected subgroups.
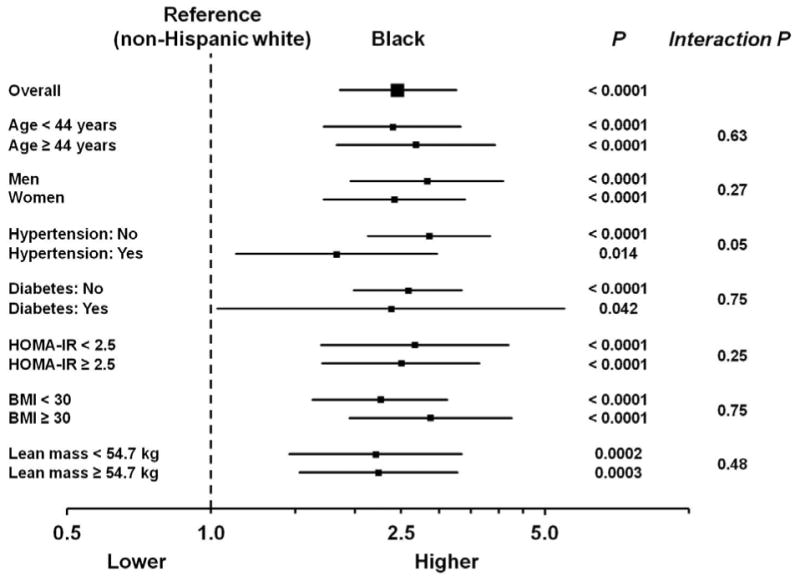
Odds ratios (95% CI) for low Nt-proBNP (defined as the lowest sex-specific quartile: ≤ 7.3 pg/ml for men; ≤ 19.4 pg/ml for women) for black compared with white individuals. Models are adjusted for race/ethnicity, age, sex, heart rate, anti-hypertensive medication use, systolic blood pressure, diabetes mellitus, body mass index, estimated glomerular filtration rate, urine microalbumin, education, and income. Analyses including HOMA-IR are restricted to individuals without diabetes mellitus. HOMA-IR = homeostatic assessment model for insulin resistance. For lean mass subgroup analyses, models included lean and fat mass in place of BMI. BMI = body mass index
