Figure 2.
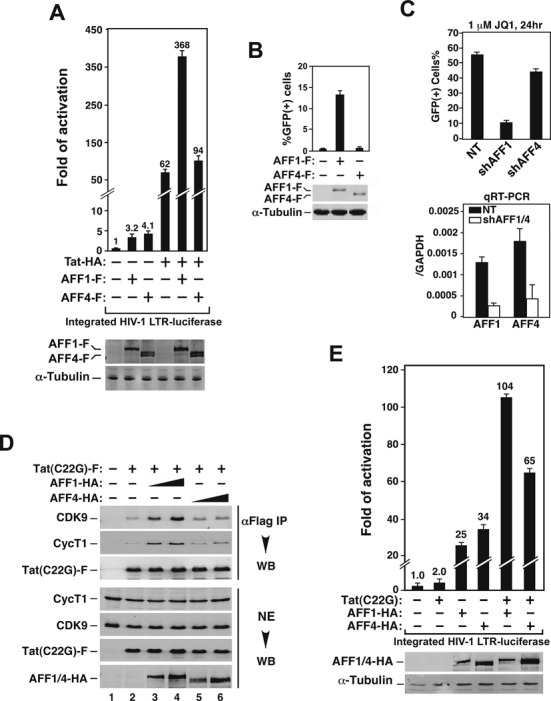
AFF1 supports Tat-dependent HIV-1 transcription more efficiently and increases the affinity of Tat for P-TEFb more potently than does AFF4. (A) Luciferase activities were measured in extracts of NH1 cells containing the integrated HIV-1 LTR-luciferase reporter gene and transfected with the Tat-HA- and/or AFF1/4-F-expressing construct as labeled. The activity in cells transfected with only the empty vectors was artificially set to 1. The error bars represent mean ± SD from three independent measurements. The cellular AFF1/4-F levels were determined by anti-Flag western blotting (WB). (B) J-Lat A2 cells were nucleofected with the AFF1/4-F-expressing construct as labeled. The induction of GFP expression was measured by flow cytometry and expressed as percentages of GFP(+) cells of the entire population. Cellular AFF1/4-F levels were detected as in A. (C) Top panel: 2D10 cells were nucleofected with plasmids expressing a non-targeting shRNA (NT) or a specific shRNA targeting AFF1 or AFF4. The activation of the HIV-1 LTR-driven GFP expression was analyzed as in B. Bottom panel: the knockdown efficiency of the shRNAs was determined by qRT-PCR, with the mRNA ratios of AFF1/4 over GAPDH displayed. (D) Nuclear extracts (NEs) from HeLa cells co-transfected with the indicated expression constructs were subjected to anti-Flag immunoprecipitation (IP). The precipitates and NEs were analyzed by WB. (E) Luciferase activities expressed from the integrated HIV-1 LTR in NH1 cells that were transfected with the Tat (C22G)- and/or AFF1/4-HA-expressing construct were measured and analyzed as in A.
