Figure 1.
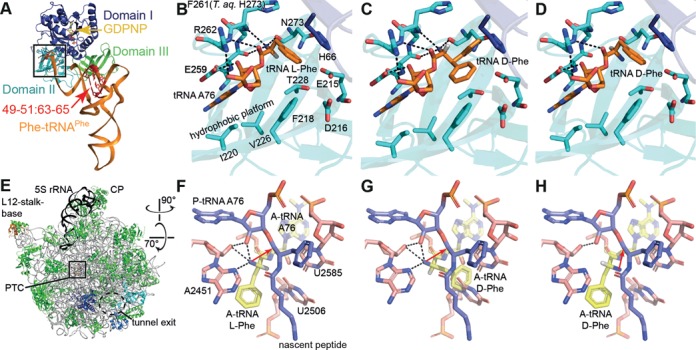
l-aa-tRNA and d-aa-tRNA bound to EF-Tu and the ribosomal A-site. (A) Structure of a TC l-Phe-tRNAPhe-EF-Tu-GDPNP. (B) Zoom into the EF-Tu amino acid binding pocket. Hydrogen bonds are indicated as dashed lines. (C, D) Models of d-Phe-tRNAPhe bound to EF-Tu. In (C), the d-Phe side chain faces steric constraints or clashes within the pocket, whereas in (D), clashes are avoided but interactions between EF-Tu and the d-Phe α-amino group are lost. (E) Cytosol side or backside view of the 50S ribosomal subunit. (F) the ribosomal PTC with an l-Phe-tRNA in the A-site. The α-amino group makes several interactions and starts a nucleophilic attack on the peptidyl-tRNA ester carbon for peptide bond formation (red arrow). (G,H) Models of d-Phe-tRNA in the A-site. In (G), the side chain clashes with U2585 and U2506, whereas in (H), the side chain can be accommodated but the α-amino group is turned into an unfavorable position for peptidyl transfer. Coordinates from PDBs 1TTT (41) and 1VQN (45).
