Fig. 3.
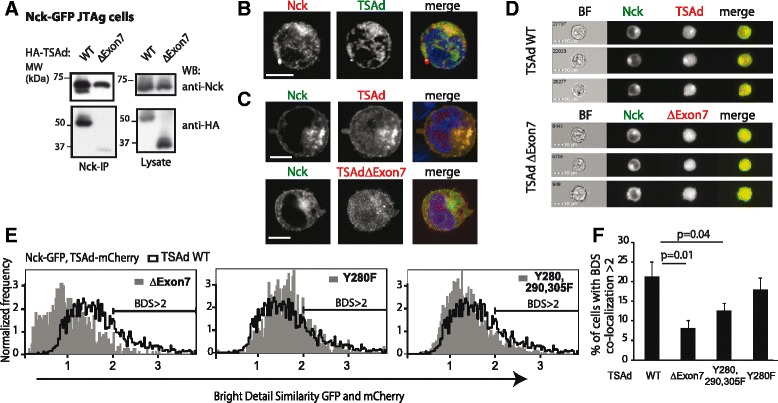
Co-localization of TSAd and Nck in T cells. a Nck co-immunoprecipitation of TSAd expressed in JTAg cells. Immunoblot of Nck-IP and lysates from JTAg cells transfected with Nck-GFP and HA-TSAd constructs. One representative of three experiments is shown. b Confocal microscopy images (60× magnification) of one CD3/28 activated human CD3+ T cell, stained with anti-Nck (red), anti-TSAd (green) and Hoechst 33342 (blue nuclear staining in the merged image). Scale bar = 5 μm. Images are representative of two independent experiments. c Confocal microscopy images (100× magnification) of transfected, fixed and permeabilized JTAg cells showing Nck-GFP (green), TSAd-mCherry (red) and merged images with nuclei staining Hoechst 33342 (blue). Images are representative of three independent experiments. Scale bar = 5 μm. d and e Co-localization of Nck-GFP and the indicated TSAd-mCherry molecules analyzed with the ImageStream cytometer, gated on double positive GFP and mCherry cells. d Gallery of representative IFC images. e Co-localization analyzed with the “Bright Detail Similarity” (BDS) algorithm in the IDEAS software. The BDS score is the log transformed Pearson's correlation coefficient of the localized bright spots with a radius of 3 pixels or less within the masked area in the two input images. Overlay of BDS histograms comparing co-localization of various TSAd molecules to Nck are shown. Data are representative of four independent experiments. f Percentage of cells that shows high degree of co-localization (BDS score >2) in (e) for Nck-GFP with each of the TSAd constructs. Graph shows mean ± standard deviation from four experiments. P-values are indicated (2-tailed paired t-test)
