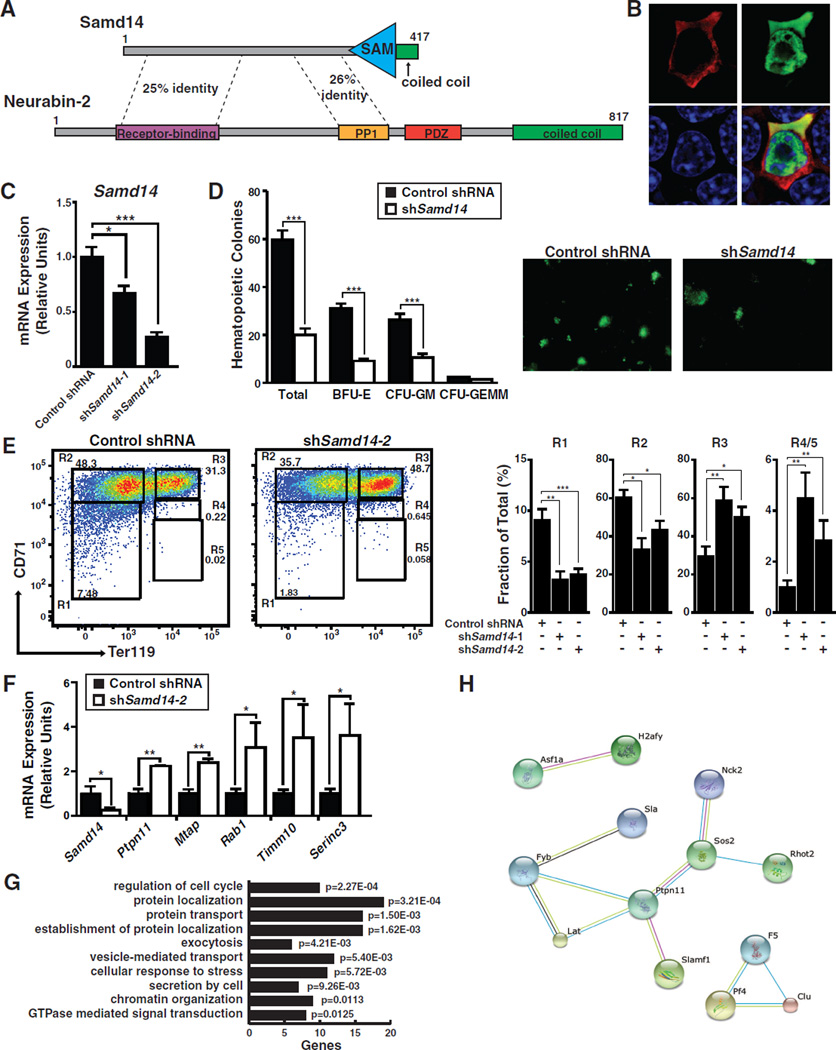
Figure 4. Samd14: a Regulator of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells.
(A) Samd14 contains a C-terminal sterile-alpha motif domain, a C-terminal α-helix, and is homologous to Neurabin-2. (B) Immunofluorescence staining of G1E cells nucleofected with pMSCV-HA-Samd14-IRES-GFP expression vector (100× magnification). (C) Retroviral-mediated shRNA knockdown of Samd14 in E14.5 fetal liver cells. (D) Quantitation of GFP+ colonies, BFU-E, CFU-GM, and CFU-GEMM and representative fluorescent images at 4× magnification. (E) Flow cytometric staining of fetal liver cells for CD71 and Ter119 retrovirally-infected with control or Samd14 shRNA expanded for 3 days. Quantitation was conducted with two different Samd14 shRNAs. (F) Real-time RT-PCR validation of RNA-seq data showing genes significantly down- and up-regulated upon Samd14 knockdown. (G) DAVID analysis of genes with significantly altered expression based on RNA-seq of FACS-sorted fetal liver R1 cells using control or shSamd14 knockdown (n=3). (H) STRING analysis of genes interacting with Ptpn11 with significant expression changes. Statistical significance: mean +/− SEM.; *, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***, p<0.001. See also Figure S2 and S3 and Table S3.