Figure 1.
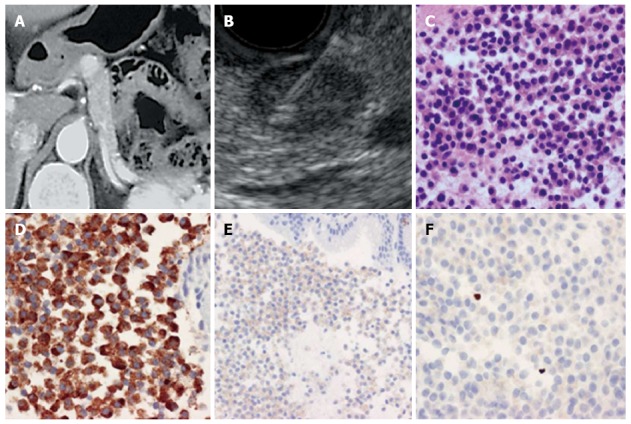
Method of endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration. A: Abdominal contrast computed tomography. An enhancing tumor was recognized in the body of the pancreas; B: EUS-FNA. The tumor was recognized as a low echoic lesion with distinct boundaries; a 22G needle was inserted into the tumor; C: A specimen obtained by EUS-FNA (HE staining). Tumor cells with oval nuclei and acidophilic granular cytoplasm proliferated diffusely; D: A specimen obtained by EUS-FNA (Chromogranin A staining). Tumor cells were Chromogranin A-positive; E: A specimen taken by EUS-FNA (CD56 staining). Tumor cells were CD56-positive; F: A specimen taken by EUS-FNA (Ki-67 antibody staining). The Ki-67 index was 0.4% with tumor grade G1. EUS-FNA: Endoscopic ultrasonography-guided fine needle aspiration.
