FIG. 9.
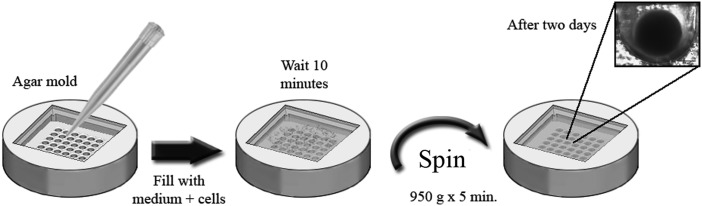
Micromold technology allows for creation of a mold in various materials to form EBs with uniform shape and size. The embryonic stem cells are digested with an enzymatic procedure and the resultant single-cell suspension is plated into the micromold made with 50 μL of low-melting-point agarose at various concentrations, depending on the sizes of the embryonic bodies to be produced. After 10 min, the cells fall into the microwells, and 950 g is applied for 5 min to force cell aggregation. After 2 days of incubation at 37°C, the cells form EBs. The obtained human embryoid bodies (hEBs) are transferred into a multiwell dish for subsequent differentiation or they may be shaken in an incubator at 37°C for 2 days to promote compaction. The mold is constructed based on the type of EB sought.