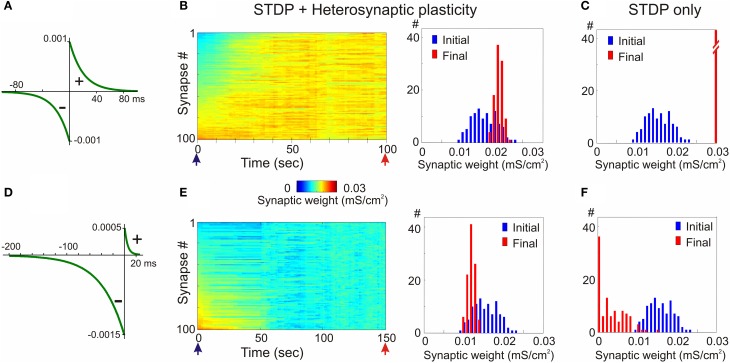
Figure 6.
Heterosynaptic plasticity prevents runaway dynamics produced by positively and negatively biased STDP. (A,D) STDP rules. STDP learning rule with symmetrical potentiation and depression windows (A, τ+ = τ− = 20 ms; a+ = a− = 10−3 mS/cm2), and with negative bias (D, τ+ = 5 ms, a+ = 0.5 × 10−3 mS/cm2, τ− = 40 ms, a− = 1.5 × 10−3 mS/cm2). (B,E) Heterosynaptic plasticity prevents runaway dynamics of synaptic weights. Same models as in Figures 2, 3 but with the mechanism for heterosynaptic plasticity as described in Chen et al. (2013). Note that in both models, with symmetrical (B) and negatively-biased (E) STDP rules, synaptic weights are not saturated, but remain normally distributed within the operation rage. (C,F) For comparison, distributions of synaptic weights in STDP only models from Figures 2, 3, expressing runaway dynamics are shown. (Modified, with permission, from Chen et al., 2013).