Figure 6. CDK8 restoration recues the defect in tumourigenesis upon Skp2 loss, and Skp2 expression is inversely correlated with mH2A1, but positively correlated with CDK8 expression in human breast cancer samples.
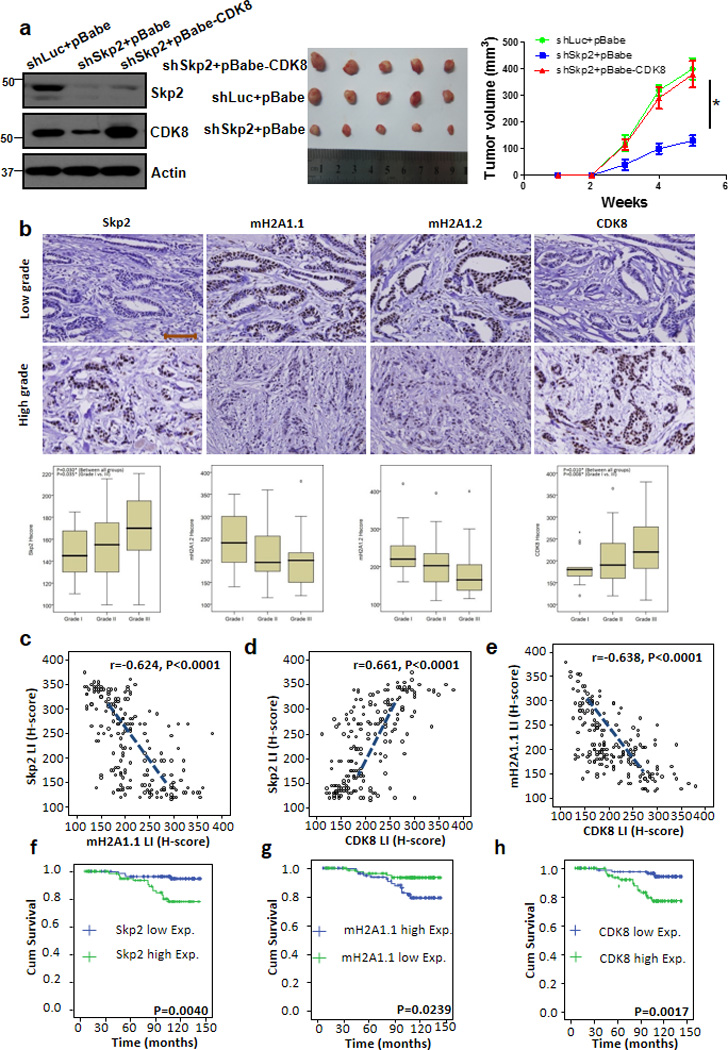
(a) Tumour volume (mm3) post-subcutaneous injections of MDA-MB-231 cells; *P < 0.05 (n=5 mice per group). MDA-MB-231 cells silenced with control, Skp2 shRNAs, or Skp2 shRNAs plus CDK8 overexpression were injected into nude mice (n=5 for each group) and followed up for tumourigenesis (see Methods). The lysate of tumour cells were subjected to immunoblotting (left panel). A photo of five tumours aligned together were presented (middle panel). The results were calculated as mean values ± s.d. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 using Student’s t-test (right panel). (b) Histological analysis of Skp2, mH2A1.1, mH2A1.2 and CDK8 expressions in patients with low or high grade of breast invasive ductal carcinoma. Scale bar represents 200µm. (c-e) Skp2 expression was negatively correlated with mH2A1.1 (r=−0.624, p<0.001) (c), but positively associated with CDK8 (r=0.661, p<0.001) (d). mH2A1.1 negatively correlated with CDK8 expression (r=−0.638, p<0.001) (e). (f-h), Kaplan-Meier plot analysis of overall survival of 189 cases of breast invasive ductal carcinoma patients with low or high expression of Skp2 (f), mH2A1.1 (g) or CDK8 (h) P-value in all case is < 0.01 by using Mann-Whitney U test.
