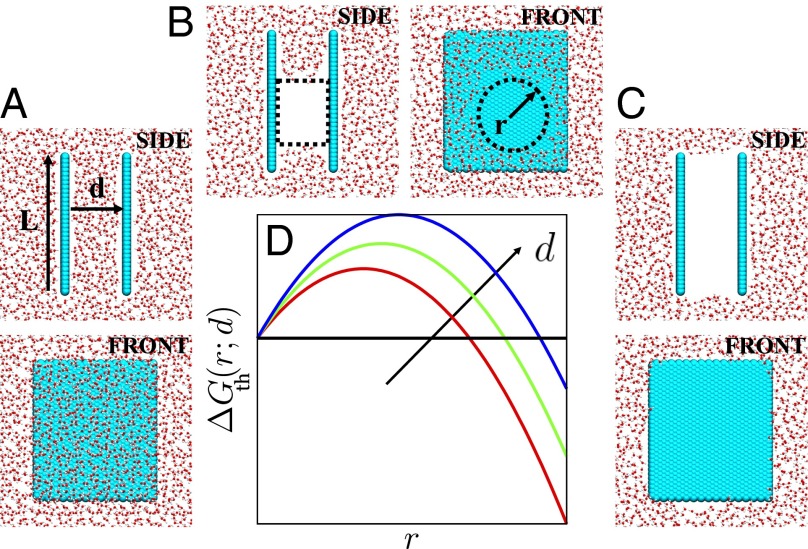
Fig. 1.
(A–C) Simulation snapshots of water (shown in red/white) in confinement between two square hydrophobic surfaces (shown in cyan) of size nm that are separated by a distance of Å; configurations highlighting (A) the liquid basin, (B) a cylindrical vapor tube of radius, r, that spans the confined region, and (C) the vapor basin are shown. In the front views, only one of the confining surfaces is shown. (D) Macroscopic theory predicts a free energetic barrier to vapor tube formation (Eq. 1), suggesting that a vapor tube larger than a critical size must be nucleated before dewetting can proceed.