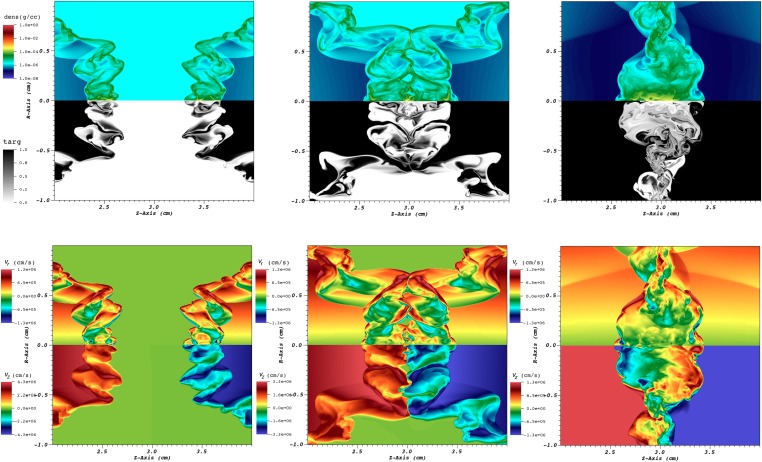
Fig. S3.
Trapping and violent turbulent mixing of the argon gas and the carbon in the jets when the two jets collide. (Upper) Close-up images of the interaction region at 600, 800, and 1,500 ns, showing the logarithm of the density (top) and the target material fraction (bottom). (Lower) Close-up images of the interaction region at the same three times, showing the radial velocity perpendicular to the axes of the jets (top) and the velocity parallel to the axes of the jets (bottom). The images show that the mixing between the argon gas and the jets is thorough and persists for µs.