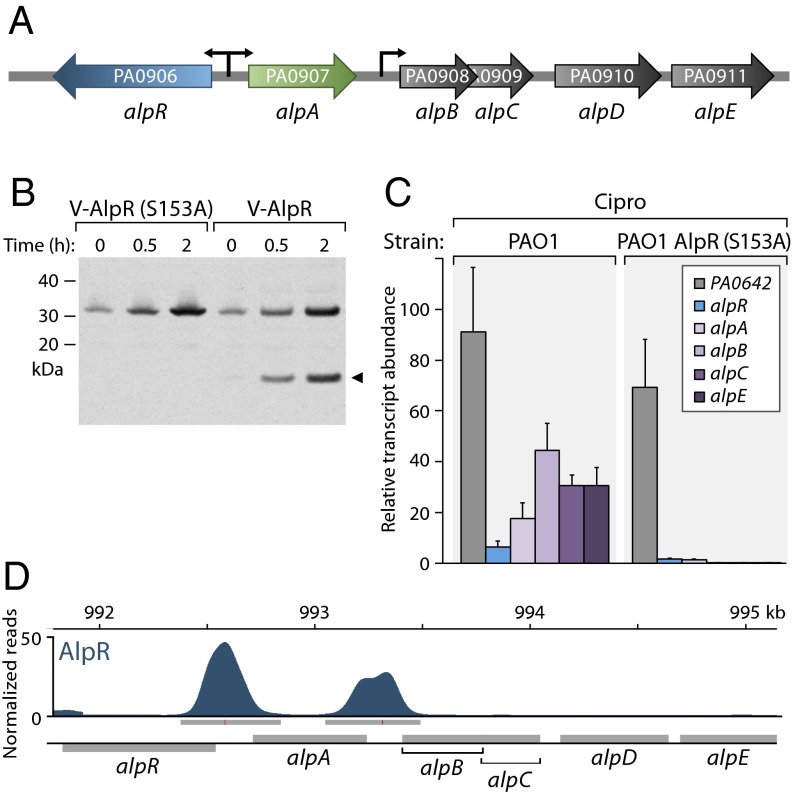
Fig. 2.
AlpR is a repressor that undergoes cleavage in response to DNA damage. (A) Schematic of alp gene cluster. (B) AlpR is cleaved in cells exposed to ciprofloxacin. Western blot analysis of AlpR with a vesicular stomatitis virus-glycoprotein (VSV-G) epitope tag fused to its N terminus (V-AlpR) and V-AlpR(S153A) following exposure of cells to ciprofloxacin for the indicated amounts of time. Arrow indicates AlpR cleavage product. (C) AlpR represses expression of the alp gene cluster. Quantification of transcript abundance by qRT-PCR in cells of the indicated strains following exposure to ciprofloxacin. Relative transcript abundance is shown in cells treated with ciprofloxacin compared with untreated cells. Expression of the PA0642 gene was induced in both the wild-type and AlpR(S153A) mutant cells, indicating that AlpR does not control the expression of all genes that are induced upon exposure to ciprofloxacin. (D) ChIP-Seq reveals that AlpR regulates the alp genes directly. ChIP-Seq with V-AlpR shows AlpR associates with the alpR-alpA and alpA-alpB intergenic regions.