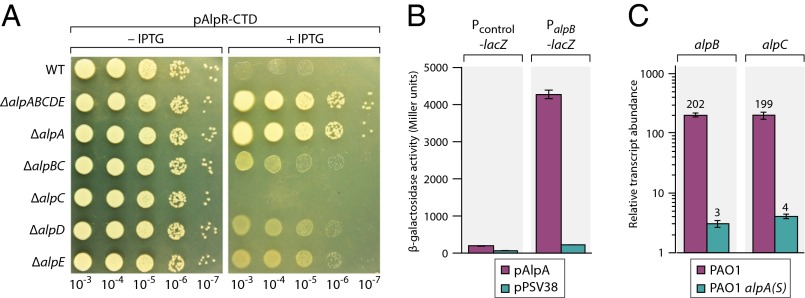
Fig. 3.
The essential function of AlpR is to repress expression of alpA, which encodes a positive regulator of the alpBCDE lysis genes. (A) Effect of ectopic synthesis of the AlpR-CTD. Wild-type and mutant PAO1 cells containing plasmid pAlpR-CTD were serially diluted and incubated on media lacking or containing IPTG. (B) AlpA positively regulates expression of an alpB promoter–lacZ fusion. Cells harboring the indicated promoter–lacZ fusions and containing plasmid pAlpA or the empty control plasmid pPSV38 were assayed for β-galactosidase activity. (C) AlpA positively regulates expression of the alpBC genes. Quantification of transcript abundance by qRT-PCR in cells following exposure to ciprofloxacin. [Cells of the PAO1 alpA(S) mutant strain contain a premature stop codon early in the alpA ORF.] Relative transcript abundance is shown in cells treated with ciprofloxacin compared with cells of the PAO1 AlpR(S153A) mutant strain treated with ciprofloxacin.