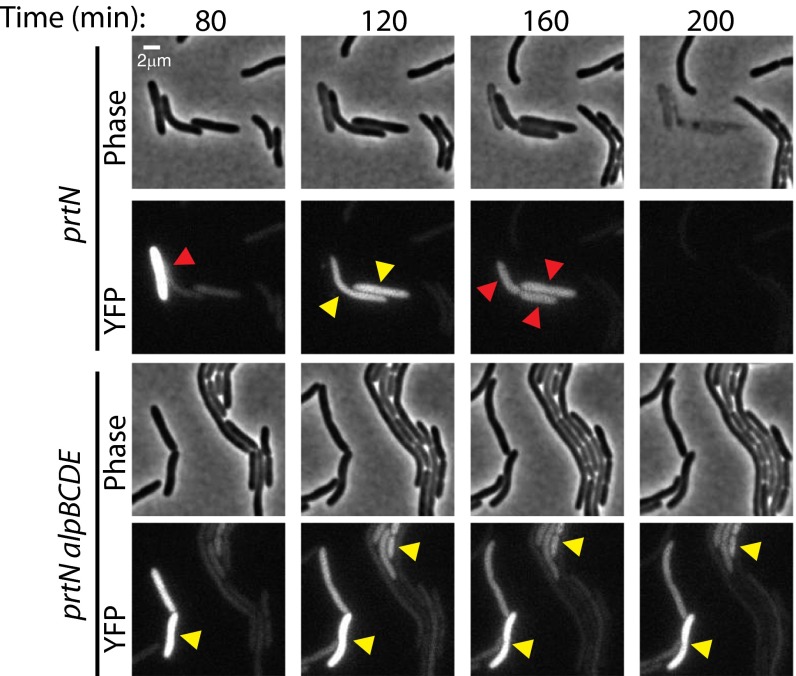
Fig. 4.
Induction of the Alp system occurs in a subset of cells treated with a DNA-damaging agent and results in alpBCDE-dependent cell lysis. Representative cropped regions from TLFM image sequences of ΔprtN mutant cells and ΔprtN ΔalpBCDE mutant cells containing an alpB promoter–yfp fusion following exposure to ciprofloxacin. The addition of ciprofloxacin resulted in induction of alpB promoter activity in a subset of cells. Expression of the alpB promoter–yfp fusion was not induced in cells that were not exposed to ciprofloxacin (Movies S9 and S11). Yellow arrowheads point to alp-induced cells; red arrowheads point to cells that undergo lysis in the subsequent frame. Cells of the ΔprtN mutant strain in which the yfp reporter was induced lysed (Upper). Cells of the ΔprtN ΔalpBCDE mutant strain in which the yfp reporter was induced did not lyse (Lower). Images were normalized for background fluorescence. (Scale bar, 2 µm.)