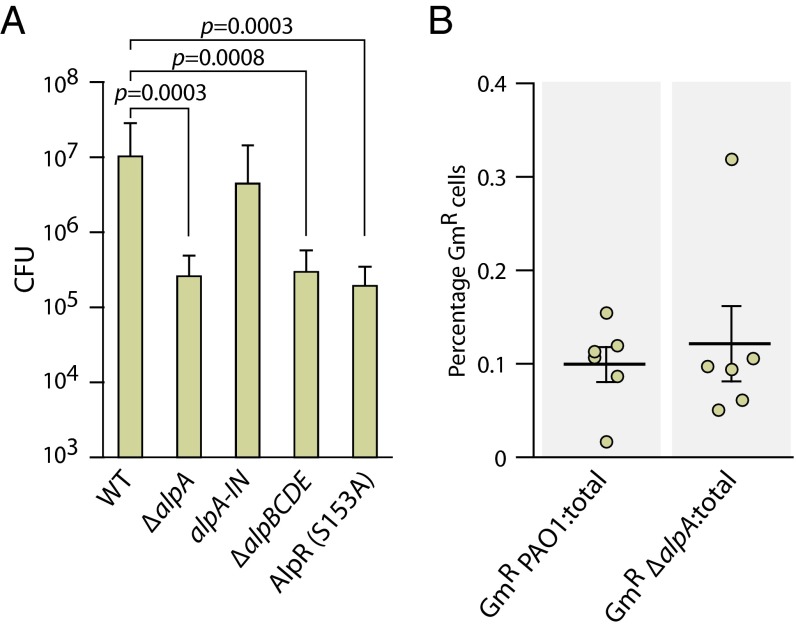
Fig. 5.
The AlpR-regulated PCD pathway promotes P. aeruginosa colonization of the murine lung. (A) Ability of the indicated strains to colonize the murine lung. Male C57BL/6 mice were inoculated via the oropharyngeal route with equivalent numbers of wild-type PAO1 cells and the indicated mutant derivatives. Graphs indicate the mean and error bars indicate SD. After 24 h mice were killed and CFUs in the lungs were enumerated. (B) Ability of the indicated marked strains to colonize the murine lung when mixed with an excess of wild-type cells. PAO1 cells marked with a gentamicin-resistance cassette (GmR PAO1) and PAO1 ΔalpA cells marked with a gentamicin resistance cassette (GmR ΔalpA) were each mixed with an excess of unmarked wild-type PAO1 cells and inoculated into male C57BL/6 mice via the oropharyngeal route. After 24 h mice were killed and the percent gentamicin-resistant (GmR) cells compared with the total number of cells in the lungs was determined. Experiments were performed twice with similar results. A representative dataset is shown.