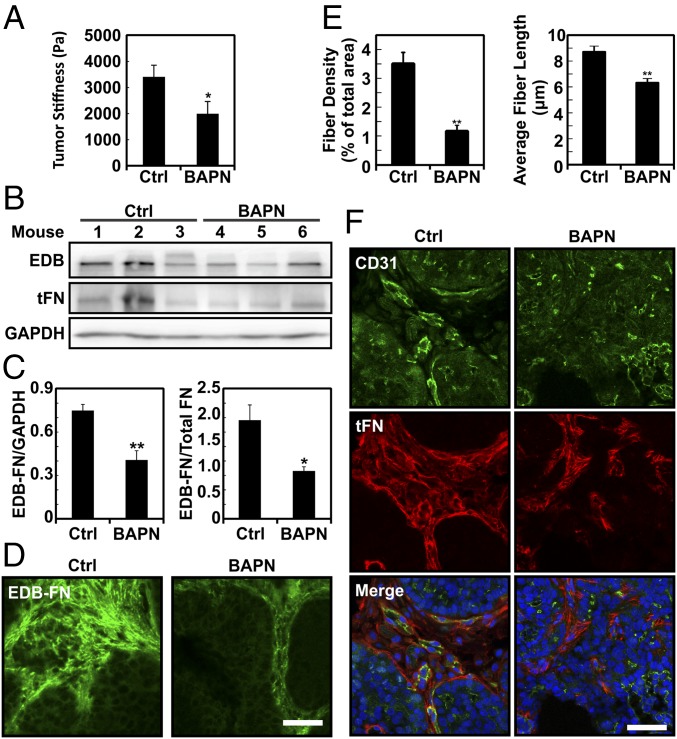
Fig. 2.
Effects of BAPN modulation of in vivo stiffness on EDB-FN in mammary tumors. (A) Mechanical measurements performed on tumor tissue from PyMT mice by unconfined compression reveal that BAPN significantly lowers tissue stiffness compared with the mock treatment (water only, Ctrl). (B) Western blotting of cancerous tissue total protein extracts from PyMT mice given either the mock treatment or treated with BAPN showing EDB-FN and total FN. GAPDH was used as loading control. (C) Corresponding densitometric quantification showing both EDB-FN normalized against GAPDH content and the ratio of EDB-FN to total FN. (D) Confocal images of EDB-FN stained frozen tissue sections with or without BAPN treatment and (E) the corresponding quantification of the average EDB-FN fiber-like structures length and content. (F) Representative confocal images of total FN and CD31 with or without BAPN treatment. Plots are mean ± SE, Student t test: *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. (Scale bars, 30 μm.)