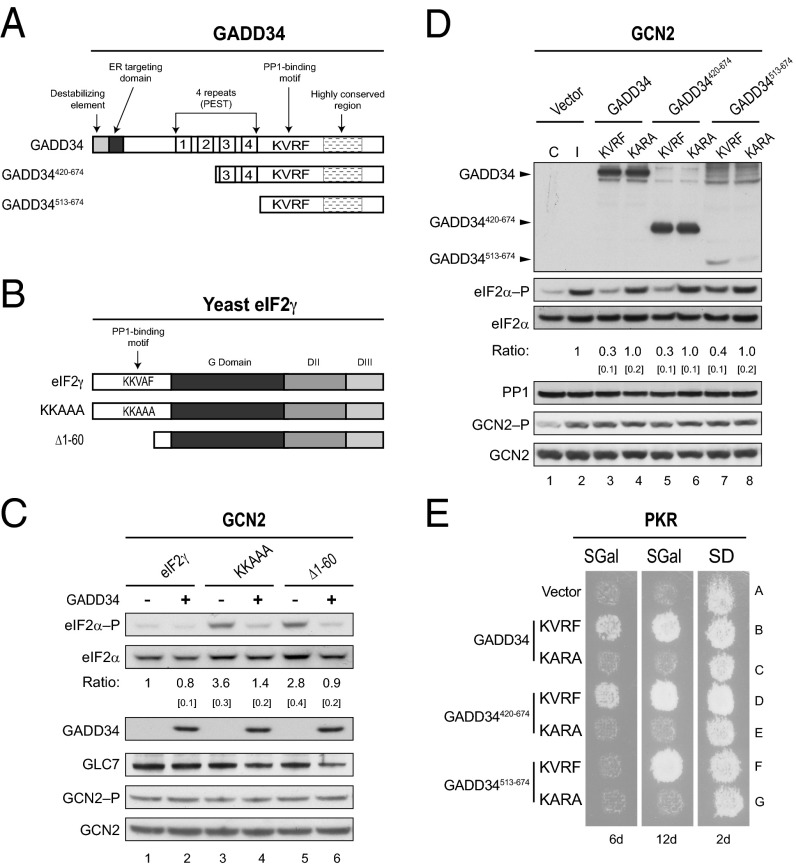
Fig. 1.
GADD34 promotes eIF2α dephosphorylation in yeast. (A) Schematics of GADD34 and two N-terminally truncated derivatives. Positions of the ER targeting domain, destabilizing element, four repeated sequence elements, PP1-binding motif (KVRF sequence), and the highly conserved region are indicated. (B) Schematic diagram showing S. cerevisiae eIF2γ. The PP1-binding motif (KKVAF sequence) in the N-terminal extension of eIF2γ, the locations of the GTP-binding (G) domain and domains II (DII) and III (DIII), and eIF2γ mutations designed to alter or eliminate the KKVAF motif are indicated. (C) Derivatives of yeast strain YM103 expressing eIF2γ, or its KKAAA or Δ1–60 derivative, and carrying either an empty vector (-) or a plasmid expressing GADD34 (+) under the control of a galactose-inducible promoter were grown in synthetic galactose (SGal) medium to log phase under nonstarvation conditions, and then equivalent amounts of WCEs were subjected to SDS/PAGE, followed by immunoblot analysis with antibodies to detect phosphorylated eIF2α–P. The membrane was then sequentially stripped and probed with antibodies against total yeast eIF2α (SUI2), the Myc-tag on GLC7, and the Flag-tag on GADD34. The relative level of phosphorylated to total eIF2α was determined by quantitative densitometry by using ImageJ software and normalized to the ratio obtained in lane 1, mean and SEs (in brackets) were calculated from at least three independent experiments. GCN2 was immunoprecipitated from yeast and subjected sequentially to immunoblot analysis by using antibodies against phosphorylated Thr882–P or total GCN2. (D) The humanized yeast strain YM100 expressing human eIF2α and human PP1 in place of yeast eIF2α (SUI2) and GLC7 was transformed with empty vector or plasmids expressing the indicated variant of GADD34. Cells were grown in SGal medium and then incubated for 1 h under nonstress control (C) conditions (lane 1) or in the presence of 1 μg/mL SM to induce (I) activation of GCN2 (lanes 2–8); equivalent amounts of WCEs were subjected to sequential immunoblot analysis by using phosphospecific antibodies against phosphorylated Ser51 of eIF2α (eIF2α–P), monoclonal antibodies against the Myc-tag on human eIF2α, monoclonal antibodies against the Flag-tag on GADD34, and monoclonal antibodies against human PP1. GCN2 was immunoprecipitated and analyzed as described for C. The relative levels of phosphorylated to total eIF2α were determined as described above. (E) Transformants of yeast strain YM77 (+PKR) bearing an empty vector or a plasmid that expresses the indicated version of GADD34 were grown to confluence on synthetic dextrose (SD) plates and then replica-plated to SD plates or SGal plates to induce PKR and GADD34 expression. To limit the appearance of revertants, plates were incubated at 18 °C for 6 or 12 d.