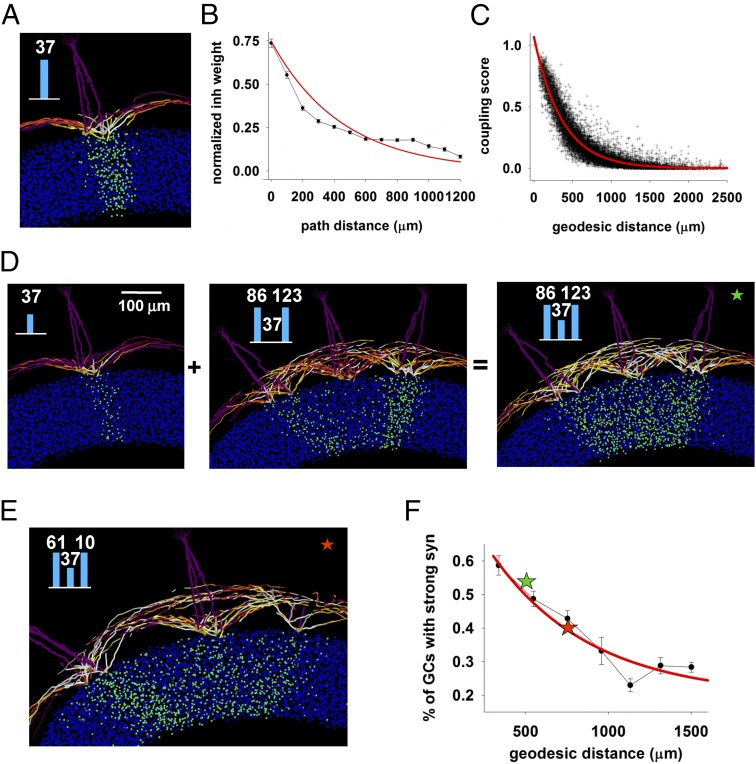
Fig. 3.
Columns interact in a predictable distance-dependent way. (A) Column formed under glomerulus 37 when activated alone, repeated here from Fig. 1E. (B) Normalized average inhibitory weight on MC dendrites as a function of distance from soma, from the simulation shown in A; the red line is a fitting of the data with an exponential function. (C) Coupling score between two glomeruli; the red line is a fit to an exponential. (D) Neighboring glomeruli can cooperate to promote formation of a column by a weakly activated glomerulus: (Left) column below glomerulus 37 formed during a weak input presentation; (Middle) activation of two neighboring glomeruli (86 and 123) did not generate any column below glomerulus 37; (Right) coactivation of all glomeruli resulted in a stronger column below glomerulus 37; bar plot in the inset represent glomerular input. (E) Coactivation of more distant glomeruli (61 and 10) resulted in a less pronounced increase of the column below glomerulus 37. (F) Simulation findings for the average interaction between glomerulus 37 and two other glomeruli at different average distance; for each bin, the average interaction was calculated as the percentage of strong GCs synapses inside a 50-μm rectangular box centered below glomerulus 37; colored stars represent the cases in E and F.