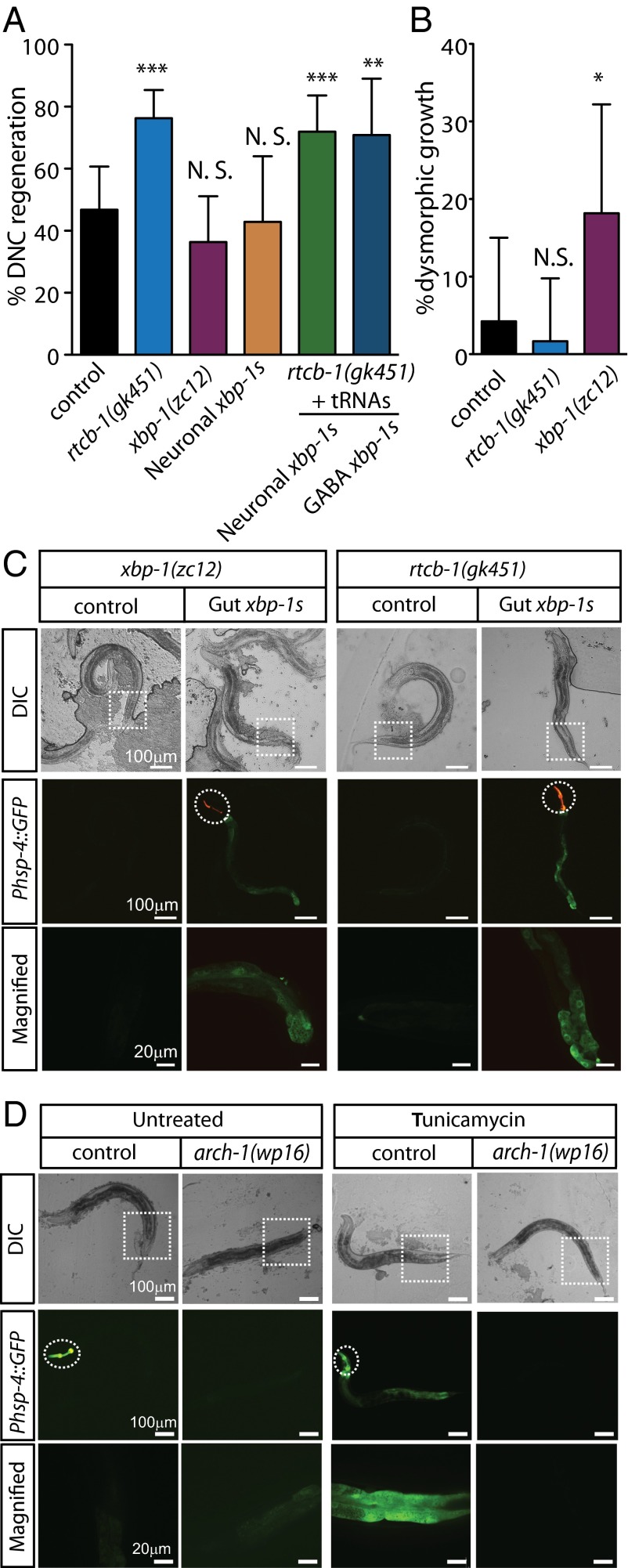
Fig. 3.
RtcB inhibits axon regeneration independently of its role in the UPR. (A) Percentage of axons that regenerated back to the DNC after 24 h. Number of axons cut per genotype from left to right: 47, 59, 44, 21, 57, and 24. (B) Percentage of axons showing dysmorphic growth in WT, rtcb-1(gk451) mutants, and xbp-1(zc12) mutants. Number of axons cut per genotype from left to right: 47, 59, and 44. (C, Top) Differential interference contrast (DIC) and (C, Middle and Bottom) fluorescence micrographs of mutant animals either without or with prespliced xbp-1 (xbp-1s) expression in gut under the regulation of spl-1 promoter. Dashed circles indicate GFP expression from injection markers in the pharynx. Dashed squares indicate corresponding magnified regions in Bottom. (D, Top) DIC and (D, Middle and Bottom) fluorescence micrographs of arch-1(wp16) mutants expressing the Phsp-4::GFP UPR reporter; arch-1 heterozygous control animals express the Phsp-4::GFP UPR reporter on treatment with tunicamycin, but arch-1(wp16) homozygote animals fail to activate the reporter. Dashed circles indicate the Pmyo-2::GFP balancer used to identify heterozygous arch-1(wp16) mutants. Error bars indicate 95% confidence interval. NS, not significant; *P < 0.05; **P < 0.005; ***P < 0.0005.