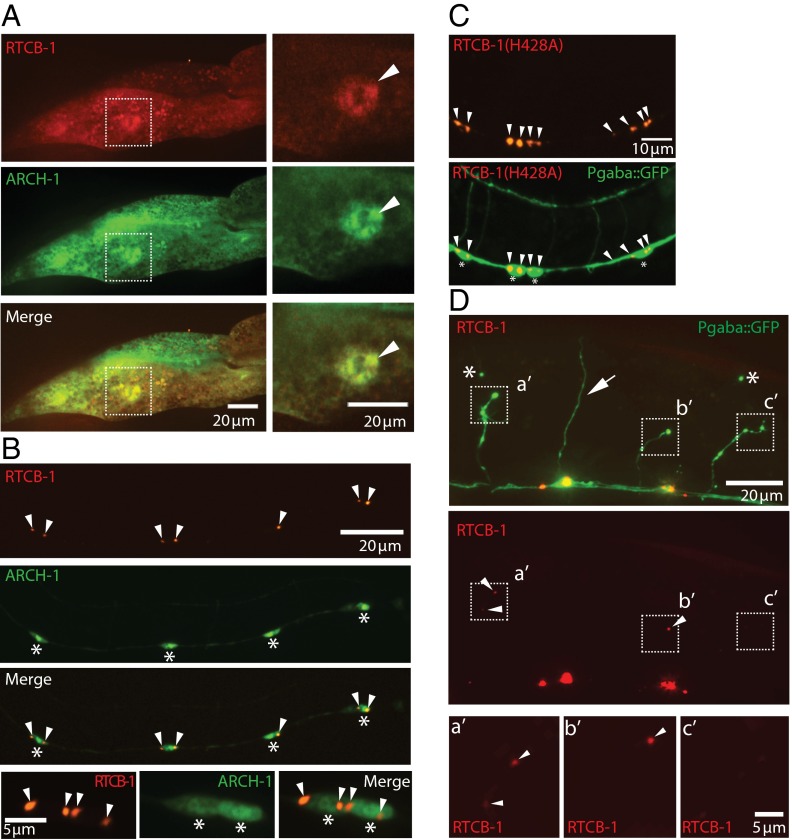
Fig. 4.
RtcB exhibits injury-dependent localization in the GABA motor neurons. (A) Expression of RFP-tagged WT RTCB-1 and GFP-tagged ARCH-1 in the intestine. Both RTCB-1 and ARCH-1 are diffusely localized in the cytoplasm and nucleus. The dashed squares in Left are magnified in Right. Arrowheads indicate the expression of RTCB-1 and ARCH-1 in the nucleus of the gut. Similar localization was observed in all animals in multiple transgenic lines (two of two lines; >10 animals for each). (B) Expression of RFP-tagged WT RTCB-1 and GFP-tagged ARCH-1 in the GABAergic neurons. ARCH-1 is robustly expressed throughout the cell bodies, including the nucleus. In contrast, RTCB-1 shows punctate localization at the perinuclear area. Row 4 shows the magnified images of rows 1–3. Arrowheads indicate RFP-tagged RTCB-1. Similar localization was observed in all animals in multiple transgenic lines (two of two lines; >10 animals for each). *Cell bodies. (C) Localization of catalytically inactive RTCB-1 (H428A) in the GABAergic neurons. Arrowheads indicate RFP-tagged RtcB. Similar localization was observed in all animals in multiple transgenic lines (two of two lines; >10 animals for each). *Cell bodies. (D) Expression of WT RTCB-1 in the GABAergic neurons at 20 h after injury. The dashed squares indicate the tips of injured axons that are magnified in Bottom. The arrow indicates the intact axon. Arrowheads indicate accumulated RFP-tagged RTCB-1 near the injured axon tips. RFP was detected in 21 of 27 severed axons (78%; 95% confidence interval is 59–90%). *Distal stump as evidence of axotomy.