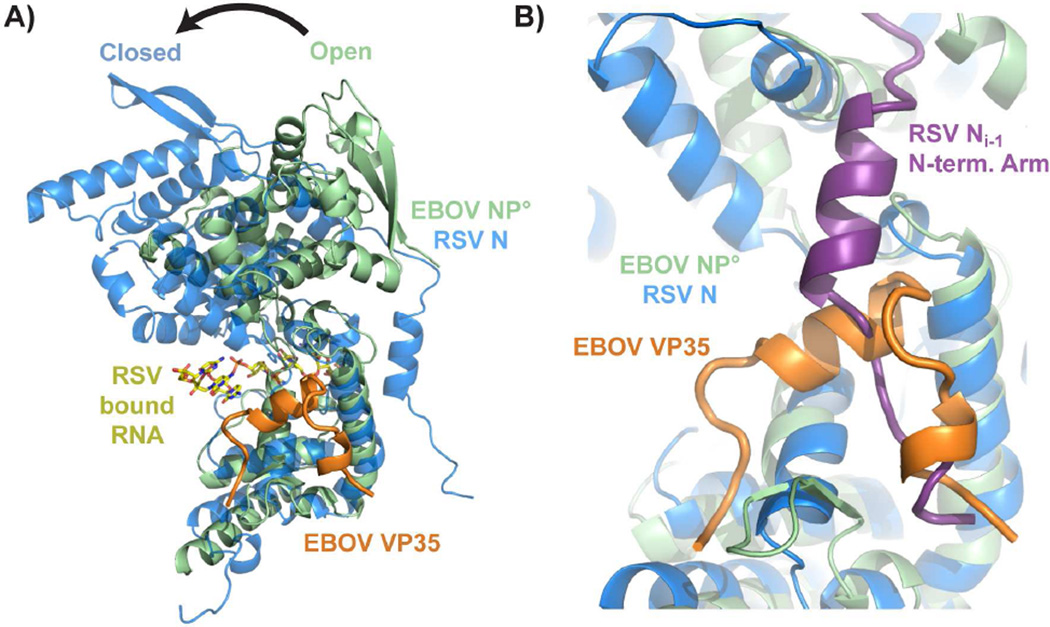
Figure 4. Comparison of the Ebola virus NP°-VP35 complex with the respiratory syncytial virus N-RNA complex.
A) Chain A of PDB 2WJ8 was superimposed onto the Ebola virus NP° core domain-VP35 N-terminal peptide complex using the nucleoprotein C-terminal domains. A transition from the open state (monomeric EBOV NP) to the closed state (oligomeric RSV N) is likely necessary to form the RNA-binding site, which is not occluded by the EBOV VP35 peptide. B) The EBOV VP35 N-terminal peptide occupies the site on EBOV NP° core that is bound by the N-terminal oligomerization arm of an adjacent nucleoprotein (NPi−1) in the oligomeric RSV N structure. For a structural alignment of the individual N- and C-terminal domains of RSV and EBOV NP, see figure S4.