Fig. 6.
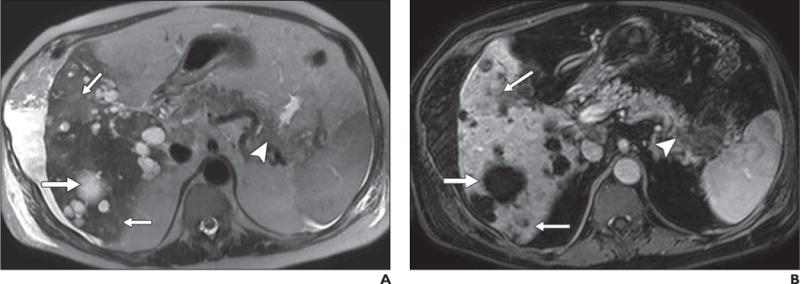
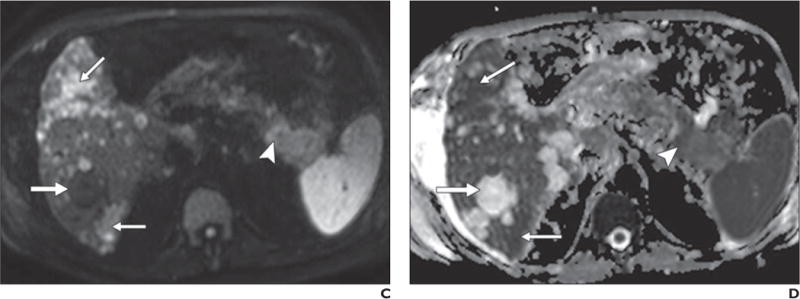
67-year-old man with history of polycystic kidney disease and T3NxMx gallbladder cancer.
A–D, In T2-weighted single-shot fast spin-echo image (A), gadolinium-enhanced T1-weighted spoiled gradient-echo image obtained during venous phase (B), diffusion-weighted image with b800 (C), and apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) map (D), mass is seen in tail of pancreas (arrowhead), which was biopsy-proven to be adenocarcinoma. Numerous well-demarcated lesions are noted in liver (thick arrow) with homogenous high signal intensity on T2-weighted images, low signal intensity on diffusion-weighted b800 images, and high signal intensity on ADC map; these are consistent with simple cysts related to polycystic kidney disease and represent challenge for detection of metastatic disease. Subtle areas of high signal intensity relative to background liver are noted on T2-weighted images (thin arrows, A) with mild hypo-enhancement (thin arrows, B) but are far more conspicuous on diffusion-weighted image (thin arrows, C). Low signal intensity in these lesions on ADC map (thin arrows, D) in conjunction with contrast-enhanced images, helps to characterize these as solid lesions. Findings were suspicious for hepatic metastatic disease.
