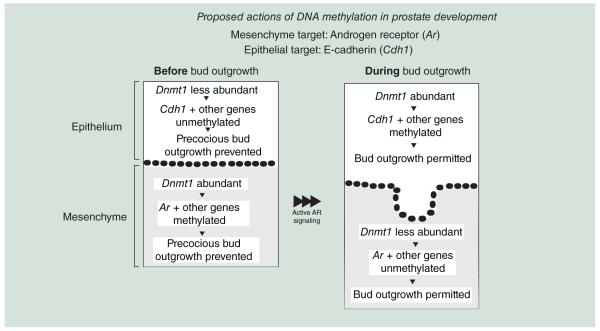
Figure 2. Proposed mechanisms of action for DNA methylation during prostate development.
Early in prostate development, when DNA methyltransferase expression predominates in mesenchyme, DNA methylation of Ar acts to constrain prostate bud formation and prevents precocious growth. Later in development, when Dnmts predominates in epithelium, DNA methylation of Cdh1 facilitates prostate epithelial differentiation and outgrowth.
Ar: Androgen receptor; Cdhl: E-Cadherin.