Abstract
Nuclear proteins are targeted through the nuclear pore complex (NPC) in an energy-dependent reaction. The import reaction is mediated by nuclear localization sequences (NLS) in the substrate which are recognized by heterodimeric cytoplasmic receptors. hSRP1 alpha is an NLS-binding subunit of the human NLS receptor complex and is complexed in vivo with a second subunit of 97 kDa (p97). We show here that a short amino-terminal domain in hSRP1 alpha is necessary and sufficient for its interaction with p97. This domain is conserved in other SRP1-like proteins and its fusion to a cytoplasmic reporter protein is sufficient to promote complete nuclear import, circumventing the usual requirement for an NLS receptor interaction. The same amino-terminal domain inhibits import of NLS-containing proteins when added to an in vitro nuclear transport assay. While full-length hSRP alpha is able to leave the nucleus, the amino-terminal domain alone is not sufficient to promote exit. We conclude that hSRP1 alpha functions as an adaptor to tether NLS-containing substrates to the protein import machinery.
Full text
PDF




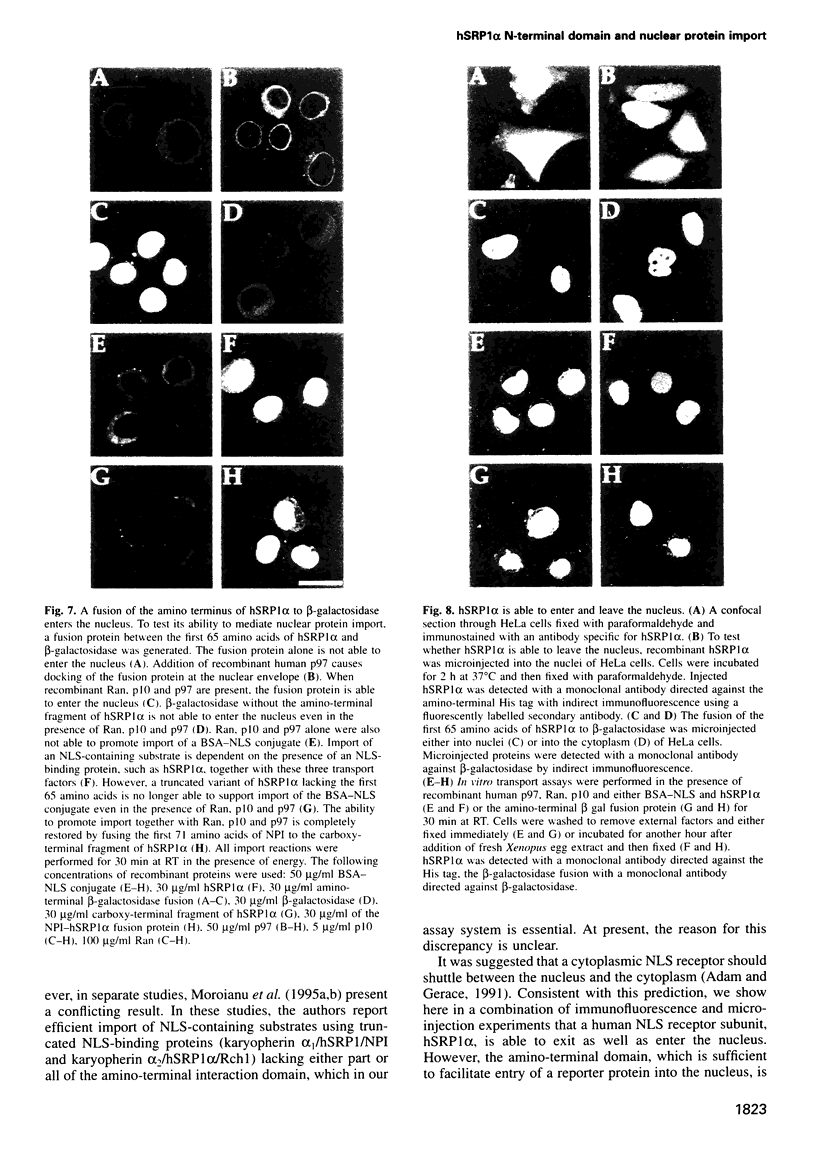


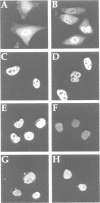
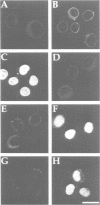
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adam E. J., Adam S. A. Identification of cytosolic factors required for nuclear location sequence-mediated binding to the nuclear envelope. J Cell Biol. 1994 May;125(3):547–555. doi: 10.1083/jcb.125.3.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A., Gerace L. Cytosolic proteins that specifically bind nuclear location signals are receptors for nuclear import. Cell. 1991 Sep 6;66(5):837–847. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90431-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Adam S. A., Marr R. S., Gerace L. Nuclear protein import in permeabilized mammalian cells requires soluble cytoplasmic factors. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):807–816. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.807. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cortes P., Ye Z. S., Baltimore D. RAG-1 interacts with the repeated amino acid motif of the human homologue of the yeast protein SRP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Aug 2;91(16):7633–7637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.16.7633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuomo C. A., Kirch S. A., Gyuris J., Brent R., Oettinger M. A. Rch1, a protein that specifically interacts with the RAG-1 recombination-activating protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):6156–6160. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.6156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasso M. RCC1 in the cell cycle: the regulator of chromosome condensation takes on new roles. Trends Biochem Sci. 1993 Mar;18(3):96–101. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(93)90161-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drivas G. T., Shih A., Coutavas E., Rush M. G., D'Eustachio P. Characterization of four novel ras-like genes expressed in a human teratocarcinoma cell line. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;10(4):1793–1798. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.4.1793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enenkel C., Blobel G., Rexach M. Identification of a yeast karyopherin heterodimer that targets import substrate to mammalian nuclear pore complexes. J Biol Chem. 1995 Jul 14;270(28):16499–16502. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.28.16499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Henklein P., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. A 41 amino acid motif in importin-alpha confers binding to importin-beta and hence transit into the nucleus. EMBO J. 1996 Apr 15;15(8):1810–1817. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Prehn S., Laskey R. A., Hartmann E. Isolation of a protein that is essential for the first step of nuclear protein import. Cell. 1994 Dec 2;79(5):767–778. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90067-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Görlich D., Vogel F., Mills A. D., Hartmann E., Laskey R. A. Distinct functions for the two importin subunits in nuclear protein import. Nature. 1995 Sep 21;377(6546):246–248. doi: 10.1038/377246a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto N., Shimamoto T., Kose S., Takao T., Tachibana T., Matsubae M., Sekimoto T., Shimonishi Y., Yoneda Y. The nuclear pore-targeting complex binds to nuclear pores after association with a karyophile. FEBS Lett. 1995 Jul 24;368(3):415–419. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(95)00699-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imamoto N., Shimamoto T., Takao T., Tachibana T., Kose S., Matsubae M., Sekimoto T., Shimonishi Y., Yoneda Y. In vivo evidence for involvement of a 58 kDa component of nuclear pore-targeting complex in nuclear protein import. EMBO J. 1995 Aug 1;14(15):3617–3626. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1995.tb00031.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izaurralde E., Lewis J., McGuigan C., Jankowska M., Darzynkiewicz E., Mattaj I. W. A nuclear cap binding protein complex involved in pre-mRNA splicing. Cell. 1994 Aug 26;78(4):657–668. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90530-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Küssel P., Frasch M. Pendulin, a Drosophila protein with cell cycle-dependent nuclear localization, is required for normal cell proliferation. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(6):1491–1507. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.6.1491. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann M., Wilm M. Electrospray mass spectrometry for protein characterization. Trends Biochem Sci. 1995 Jun;20(6):219–224. doi: 10.1016/s0968-0004(00)89019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Gerace L. Mechanisms of nuclear protein import. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;7(3):310–318. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(95)80084-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melchior F., Paschal B., Evans J., Gerace L. Inhibition of nuclear protein import by nonhydrolyzable analogues of GTP and identification of the small GTPase Ran/TC4 as an essential transport factor. J Cell Biol. 1993 Dec;123(6 Pt 2):1649–1659. doi: 10.1083/jcb.123.6.1649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. Purification of a Ran-interacting protein that is required for protein import into the nucleus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Oct 11;91(21):10212–10216. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.21.10212. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. S., Blobel G. The GTP-binding protein Ran/TC4 is required for protein import into the nucleus. Nature. 1993 Oct 14;365(6447):661–663. doi: 10.1038/365661a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Blobel G., Radu A. Previously identified protein of uncertain function is karyopherin alpha and together with karyopherin beta docks import substrate at nuclear pore complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Mar 14;92(6):2008–2011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.6.2008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moroianu J., Hijikata M., Blobel G., Radu A. Mammalian karyopherin alpha 1 beta and alpha 2 beta heterodimers: alpha 1 or alpha 2 subunit binds nuclear localization signal and beta subunit interacts with peptide repeat-containing nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Jul 3;92(14):6532–6536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.14.6532. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Newmeyer D. D., Forbes D. J. Nuclear import can be separated into distinct steps in vitro: nuclear pore binding and translocation. Cell. 1988 Mar 11;52(5):641–653. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90402-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Neill R. E., Palese P. NPI-1, the human homolog of SRP-1, interacts with influenza virus nucleoprotein. Virology. 1995 Jan 10;206(1):116–125. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(95)80026-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powers M. A., Forbes D. J. Cytosolic factors in nuclear transport: what's importin? Cell. 1994 Dec 16;79(6):931–934. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(94)90024-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Radu A., Blobel G., Moore M. S. Identification of a protein complex that is required for nuclear protein import and mediates docking of import substrate to distinct nucleoporins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Feb 28;92(5):1769–1773. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1769. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Török I., Strand D., Schmitt R., Tick G., Török T., Kiss I., Mechler B. M. The overgrown hematopoietic organs-31 tumor suppressor gene of Drosophila encodes an Importin-like protein accumulating in the nucleus at the onset of mitosis. J Cell Biol. 1995 Jun;129(6):1473–1489. doi: 10.1083/jcb.129.6.1473. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weis K., Mattaj I. W., Lamond A. I. Identification of hSRP1 alpha as a functional receptor for nuclear localization sequences. Science. 1995 May 19;268(5213):1049–1053. doi: 10.1126/science.7754385. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilm M., Shevchenko A., Houthaeve T., Breit S., Schweigerer L., Fotsis T., Mann M. Femtomole sequencing of proteins from polyacrylamide gels by nano-electrospray mass spectrometry. Nature. 1996 Feb 1;379(6564):466–469. doi: 10.1038/379466a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Oakes M., Yamaghishi M., Dodd J. A., Nomura M. Cloning and characterization of SRP1, a suppressor of temperature-sensitive RNA polymerase I mutations, in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1992 Dec;12(12):5640–5651. doi: 10.1128/mcb.12.12.5640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]