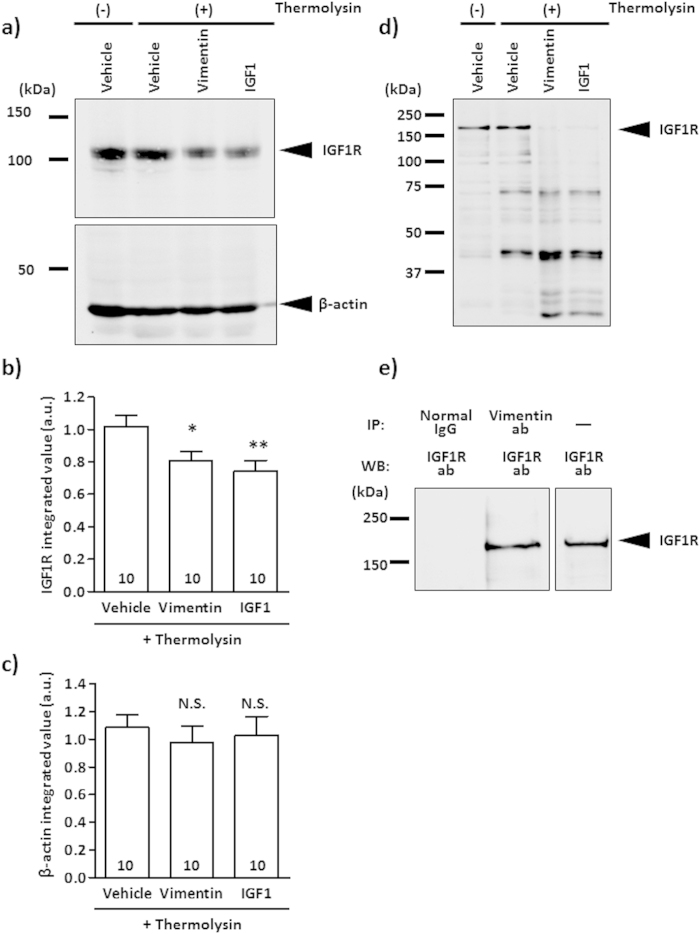
Figure 3. Vimentin binds to IGF1R directly.
(a–c) Mouse cerebral cortex (ddY, adult) lysates were treated with vimentin, IGF1 or vehicle solution and incubated for 60 min at room temperature. Then, the mixture was treated with thermolysin and run on an SDS-PAGE gel. IGF1R was detected by western blotting (a). Bands of 95 kDa were detected as IGF1R. As a negative control, β-actin (45 kDa) was measured by western blotting. Band intensities of IGF1R (b) and β-actin (c) in vimentin-treated and IGF1-treated lysates were compared with that of vehicle solution-treated lysate under thermolysin-reacted conditions. The values were calculated relative to the absence of the thermolysin group. The numbers in the columns indicate the number of experiments independently performed. (d) Recombinant IGF1R protein was treated with vimentin, IGF1 or vehicle solution and incubated for 60 min at room temperature. After treatment, the mixture was reacted with thermolysin and run on an SDS-PAGE gel. IGF1R was detected by western blotting. Bands of approximately 150 kDa were detected as IGF1R. (e) Co-incubated recombinant IGF1R (5 pmol) and vimentin (10 pmol) were immunoprecipitated with anti-vimentin antibody or normal mouse IgG, and then IGF1R was detected by western blotting. As a control, only recombinant IGF1R (0.1 pmol) without IP was loaded on the separated right lane. *p < 0.05 or **p < 0.01 vs. thermolysin-treated vehicle group with a one-way ANOVA, post hoc Dunnett’s test. N.S. indicates not significant.