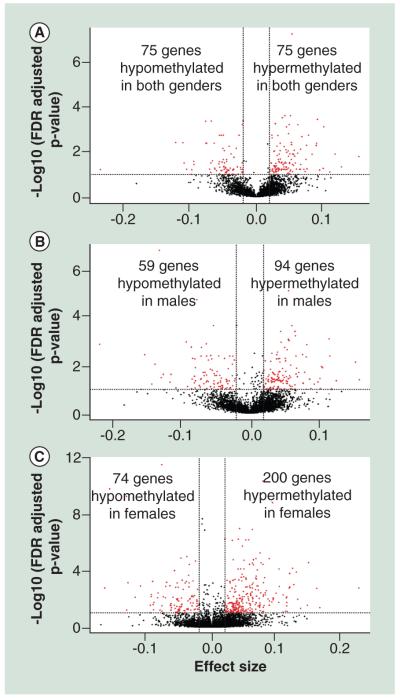
Figure 2. Lead causes common and gender-specific changes in DNA methylation.
The Pb-associated differentially methylated clusters (Pb-associated DMCs) selected for further analysis are screened by FDR cut off of 0.05 and effect size ≥∣0.02∣ or ∣2%∣ (A) A-clustering results for conserved region revealed 75 hyper-methylated Pb-associated DMCs and 41 hypo-methylated Pb-associated DMCs mapping to 76 unique genes associated with Pb exposure as predicted by the GEE model. (B) For an effect size cutoff of ∣0.02∣ or ∣2%∣, and FDR corrected P value ≤ 0.05, we found 94 Pb-associated hyper-methylated and Pb-associated 59 hypo-methylated regions mapping to 124 unique genes for males. (C) Analysis results for unique regions in females revealed 200 hyper-methylated and 74 hypo-methylated regions mapping to 201 unique genes.