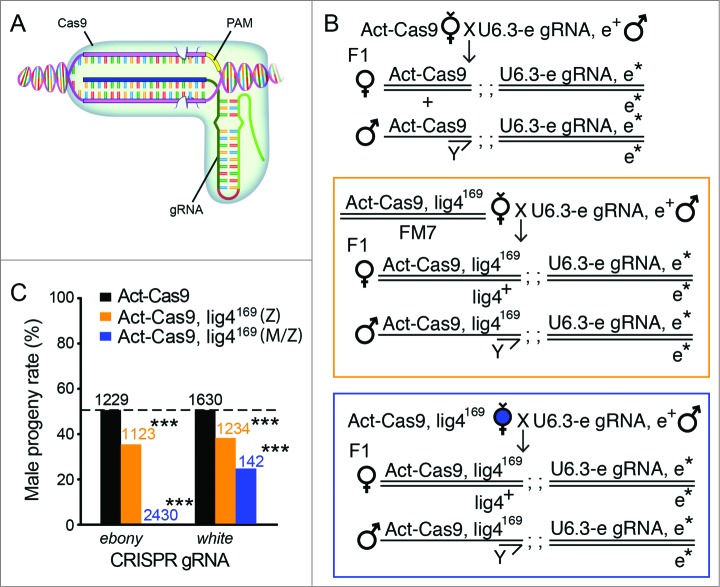
Figure 3.
Cleavage-dependent lig4169 embryo lethality with the CRISPR/Cas9 system. (A) A cartoon diagram of the CRISPR/Cas9 system, which recognizes specific DNA using a RNA/DNA/protein complex (modified from our recent review article61). The 5′ end of gRNA sequence is used for target recognition on genomic DNA around a tri-nucleotide protospacer adjacent motif (PAM). Two tooth-shape structures represent Cas9 endonuclease active sites responsible for DNA cleavage on either stand of the double strand DNA. (B) Fly genetic crossing schemes for ubiquitous gene targeting using endogenously expressed Cas9 (Act-Cas9) and gRNAs (U6.3-ebony gRNA as an example here). F1 progenies bearing both transgenes activate the CRISPR/Cas9 system ubiquitously. Bi-allelic cuts on the target gene disrupt both copies of the locus (ebony, donated with asterisk). On the middle and bottom panel, lig4169 was recombined to Act-Cas9 chromosome to assay the contribution of Lig4 in animal survival in the gene-targeted progenies. While gene targeting is predicted to be equivalently efficient in progenies of either sex, the male progeny alone in both cases are zygotic hemizygous for lig4169 mutation. Sharing the same progeny genotypes, the middle (orange box) and bottom panel (blue box) differ by their maternal genotypes: heterozygous of lig4169 for the middle panel, and homozygous of lig4169 for the bottom panel. The homozygous mothers generate both maternal and zygotic null male progenies for Lig4. (C) The percentage of male progenies surviving ubiquitous CRISPR-mediated gene targeting 2 independent loci (ebony or white gRNAs), using Act-Cas9 (blank bars); Act-Cas9, lig4169 zygotic mutant only (Z, orange bars) or Act-Cas9, lig4169 maternal and zygotic mutant (M/Z, blue bars). The statistic deviation from the theoretical 50% percent perfect ratio was tested by student t-test (***P < 0.0001).