Figure 2.
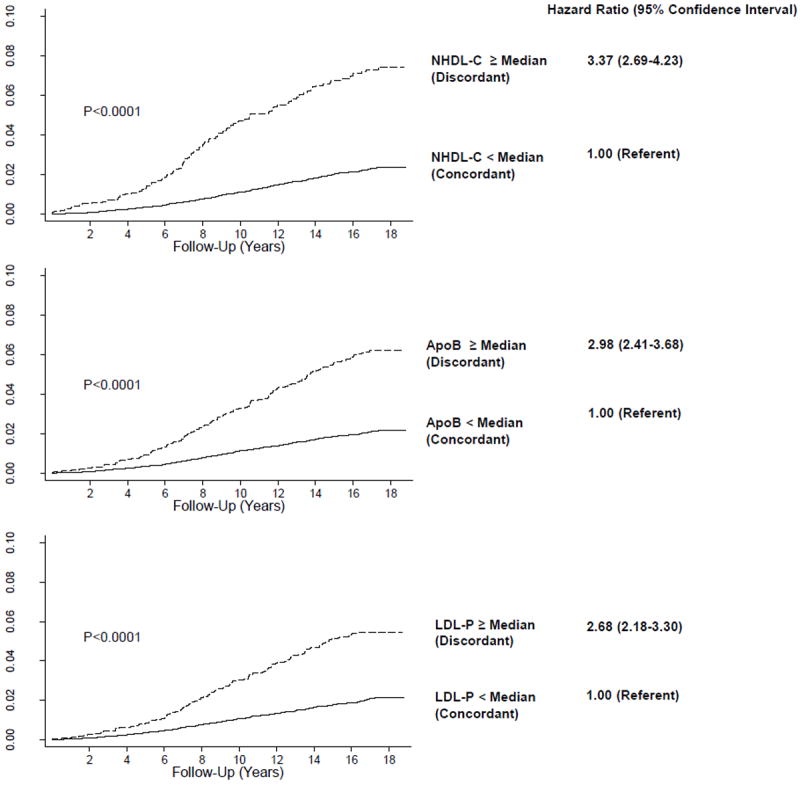
Cumulative probability of incident CHD events among 13,595 women with LDL-C < median (121 mg/dL). As shown, coronary risk is underestimated for women with discordant (≥median) levels of NHDL-C (154 mg/dL), apoB (100 mg/dL), or LDL-P (1216 nmol/L), compared with concordant levels. Hazard ratios and 95% confidence intervals obtained from Cox regression models. P for trend obtained from log-rank test.
