Figure 2.
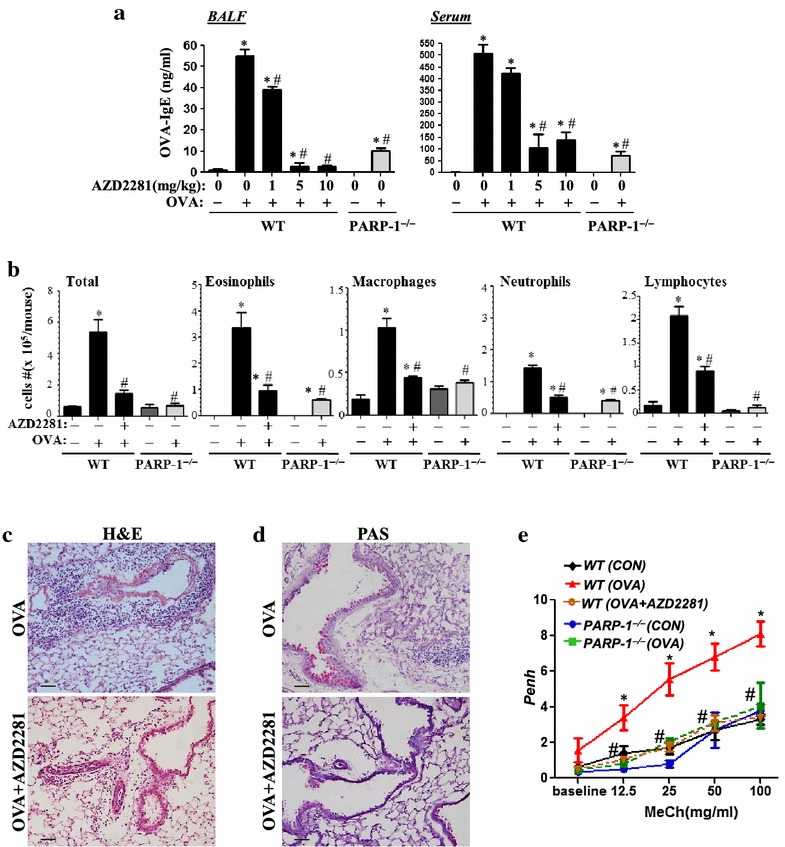
WT or PARP-1−/− mice were subjected to OVA sensitization followed by triple challenge (Multiple) or left unchallenged. WT mice were administered, i.p., 1 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg or 10 mg/kg of olaparib or saline thirty minutes after each challenge. Mice were sacrificed 48 h later and lungs were subjected to formalin fixation or BAL. a Assessment of BALF or sera collected from the different experimental groups 48 h after the last challenge for OVA-specific IgE. b Cells of BALF were differentially stained, and total cells, eosinophils, macrophages, lymphocytes, and neutrophils were counted. Data are means ± SD of values from at least six mice per group and are expressed as total number of cells per mouse. Lung sections from multiple OVA-challenged mice that were treated with either saline or olaparib were subjected to H&E c or PAS d staining. e Mice were sensitized and challenged with OVA as described above. A group of WT mice received an injection of 5 mg/kg of olaparib. Penh was recorded 24 h later using a whole body plethysmograph system before and after the indicated concentrations of aerosolized methacholine (MeCh). Results are plotted as maximal fold increase of Penh relative to baseline and expressed as mean ± SEM where n = 6 mice per group. For a, b, and e asterisk difference from control unchallenged mice, p < 0.01; hash difference from OVA-challenged mice; p < 0.01. For c and d bar 5 μm.
