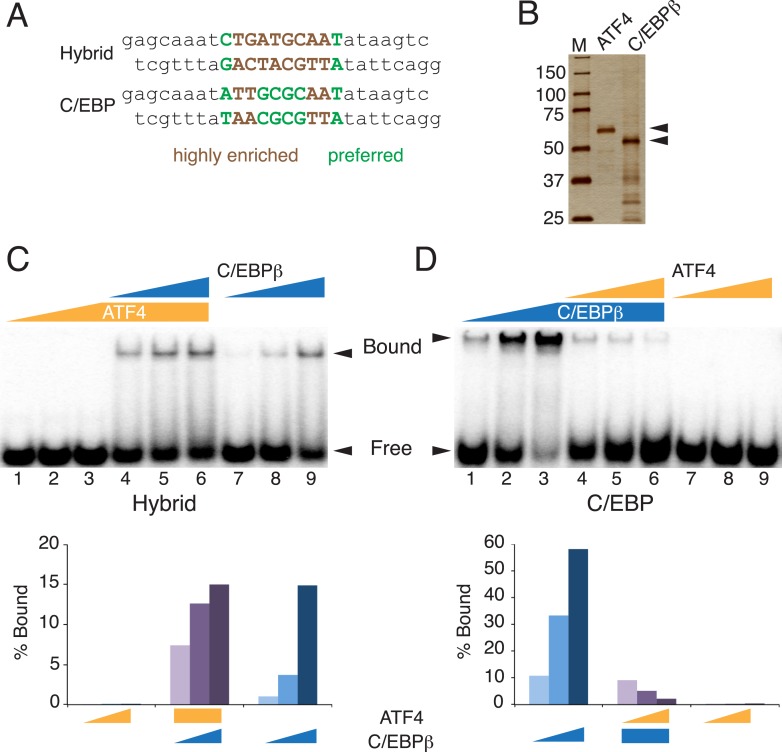
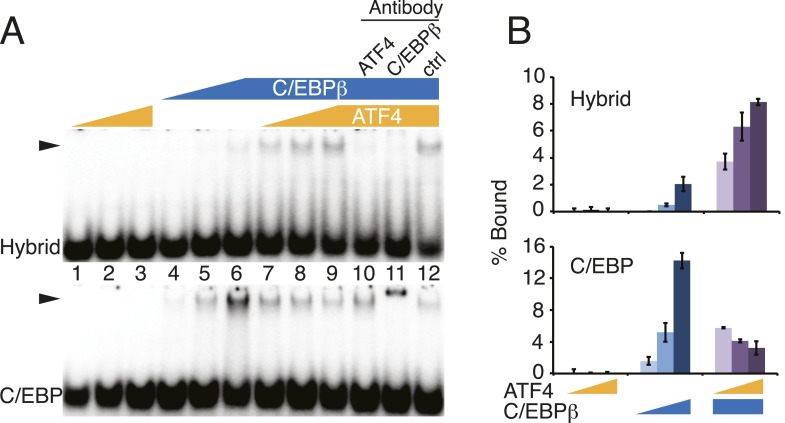
Figure 5. Distinct DNA-binding activities for ATF4, C/EBPβ and the C/EBPβ-ATF4 heterodimer.
(A) EMSA probe design for the hybrid and C/EBP sequences. Motifs are capitalized. (B) Silver-stained SDS-PAGE of recombinant his-tagged ATF4 and C/EBPβ. Arrowheads indicate the expected MWs for the tagged constructs. (C and D) EMSA titration of ATF4 (10, 30 and 90 μM) and C/EBPβ (100, 300 and 900 nM) with 0.25 nM of either the hybrid (C) or C/EBP (D) radiolabeled probe. Bar graphs show phosphoimager-based quantification of bound complexes relative to free probe.