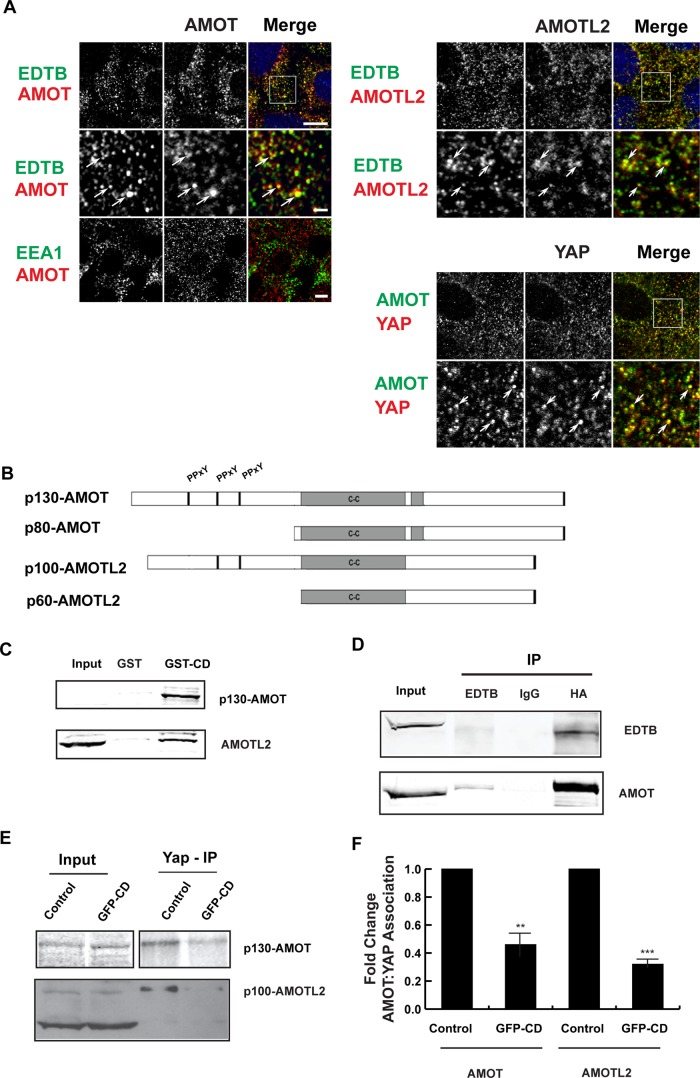
FIGURE 3:
EDTB, AMOT, and YAP all localize to endosomes, and EDTB regulates AMOT interaction with YAP. (A) Localization of endogenous AMOT, AMOTL2, YAP, EDTB, and EEA1 in MDCK cells grown on coverslips. EDTB colocalizes with AMOT (Pearson's r = 0.65) and AMOTL2 (Pearson's r = 0.79) on intracellular puncta (arrows), but there is limited colocalization with EEA1 (Pearson's r for AMOT/EEA1 is 0.18). AMOT and YAP also colocalize on intracellular puncta (Pearson's r = 0.56). Scale bars, 5 μm (top), 1 μm (insets). (B) AMOT and AMOTL2 domain structure. p80-AMOT and p60-AMOTL2 isoforms result from an internal start site. The amino-terminal domains of p130-AMOT and p100-AMOTL2 interact with YAP through the PPxY motif. (C) MDCK lysates collected at 90% confluence were used to assess the physical interaction of EDTB and AMOT/AMOTL2. Pull-down using the cytoplasmic domain of EDTB fused to GST (GST-CD) analyzed by Western blot shows interaction with AMOT and AMOTL2 relative to the GST-only control. AMOT input is sometimes not detected, indicating concentration by pull down. (D) Coimmunoprecipitation of ET-FL and HA-p130-AMOT. HEK293 cells were transfected with ET-FL and HA-p130AMOT. Lysates were immunoprecipitated with EDTB or HA antibodies. Western blot analysis shows coimmunoprecipitation of EDTB and AMOT. (E) Competition of EDTB with YAP for binding to AMOT and AMOTL2. MDCK cells expressing GFP-CD or control plasmid were immunoprecipitated with antibody against YAP and analyzed by Western blot for AMOT or AMOTL2. In the presence of GFP-CD, there is a significant decrease in the amount of AMOT and AMOTL2 associated with YAP compared with control. (F) Quantification of E. Error bars, SEM from three independent experiments. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.005.