FIGURE 4:
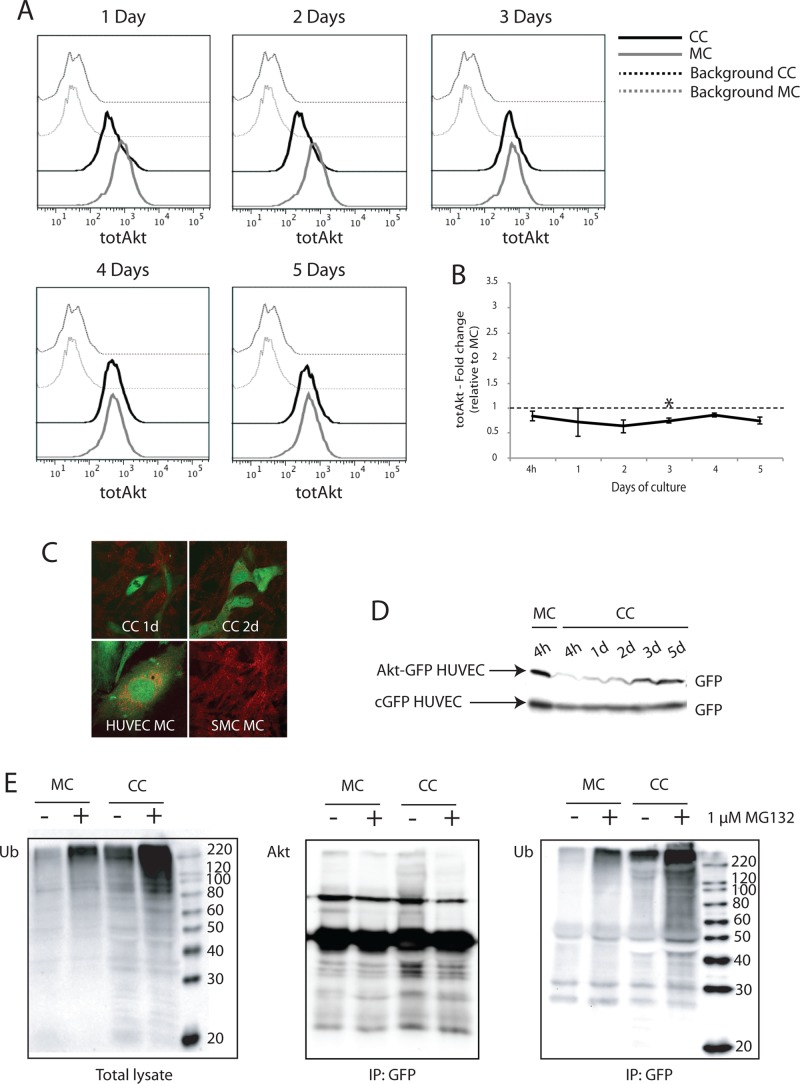
Akt is degraded by ubiquitin-dependent proteolysis in ECs cocultured with vSMCs. Total endogenous Akt level in monocultured and cocultured HUVECs was investigated by two-color flow cytometry. (A) In cocultures, total Akt was reduced in HUVECs during the first 3 d of culture. (B) Quantification of geometric mean of fluorescence from two to four independent experiments confirmed that total Akt levels were reduced relative to monocultured HUVECs (set as 1). (C) Top, endogenous Akt expression in cocultured HUVECs was also examined by confocal microscopy. Bottom, Akt (red) did not colocalize with GFP-expressing HUVECs cocultured for 1 and 2 days with PaSMCs. Monocultured HUVECs and PaSMCs both stained positive for Akt. (D) Akt expression in cocultured HUVECs was also examined by Western blot. HUVECs were transduced with an Akt-GFP fusion protein and grown in coculture. The level of GFP expression was examined in total lysates from cocultures at 4 h up to 5 d. cGFP-expressing HUVECs were used as control. Whereas Akt-GFP expression level was reduced in cocultured HUVECs during the initial 2 d of culture, cGFP expression level remained stable. (E) To investigate proteasomal degradation, cocultures and monocultures of Akt-GFP–expressing HUVECs were treated with the proteasomal inhibitor MG132 for 24 h. Akt-GFP was immunoprecipitated from total lysates using a GFP antibody. (Left) Polyubiquitinated proteins accumulated in total lysates after MG132-treatment. Postimmunoprecipitation, blots were probed with antibodies for Akt (middle) and ubiquitin (right). Cocultured HUVECs displayed increased ubiquitination of Akt-GFP compared with monocultured HUVECs both in MG132-treated and untreated samples. Asterisk indicates statistically significant differences from control (set to 1). *p < 0.05, min n = 2, max n = 4.