Figure 1.
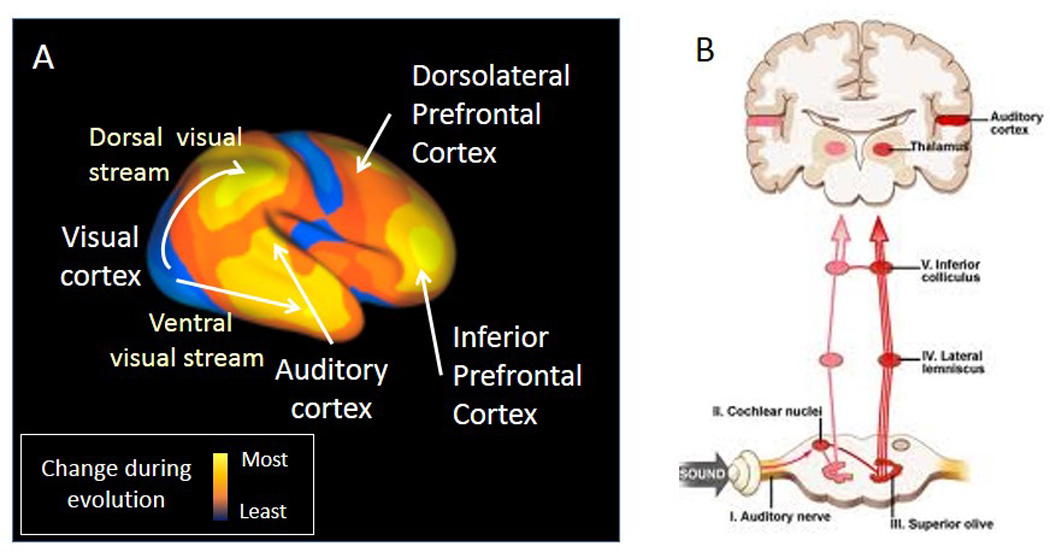
Anatomy of brain sensory systems, A. Cortical areas responsible for perception and executive function have both experienced especially enhanced expansion in the evolution of human brain (from 5). B. Right side of the brain shows auditory responses from the inner ear, conveyed through brainstem relay nuclei, arriving at the auditory cortex through the medical geniculate nucleus. Left side shows how a branch from the brainstem relay nuclei contact the reticular brainstem formation, which in turns activtes the medial septal nucleus. The medial septal nucleus cholinergic input acts in the hippocampus to help filter all the sensory information from the cortex, including auditory cortex, that is funneled to it through the Superior Temporal Gyrus.
