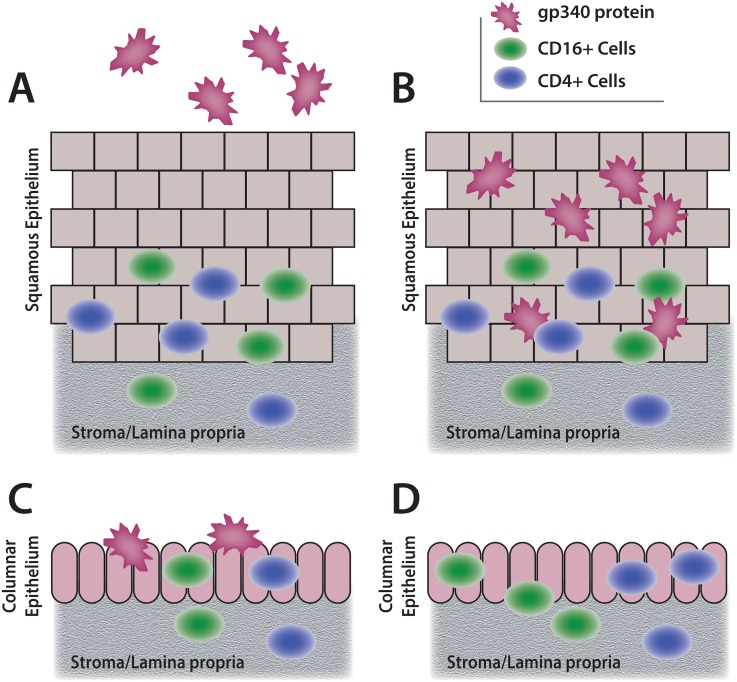
Fig 5. Schematic diagrams summarizing the observed results.
The model maps gp340 and HIV target cells at the normal mucosal surface portals. The model proposes that HIV target cells and the epithelial cell-associated alternative HIV-binding molecule gp340 rarely co-localize at the luminal surfaces lined by squamous epithelium, either oral or ectocervical, largely because the target cells typically stay away from the periluminal layer (A,B). Moreover, expression of gp340 in oral squamous epithelium appears to depend largely upon salivary glands, suggesting that it is primarily soluble (A), while the ectocervial squamous epithelium often showed strong gp340 expression throughout (B), without evidence of gp340-secreting glands. In contrast, HIV target cells and cell-associated gp340 frequently, but not always, co-localized periluminally in simple columnar epithelia of the colon/rectum and endocervix (C, D).