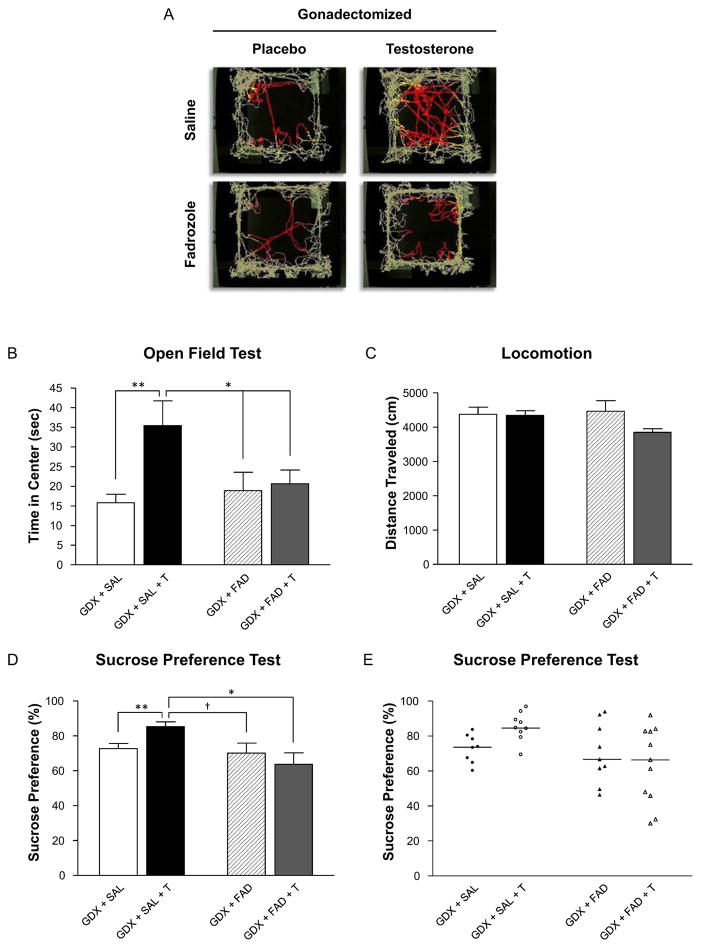
Figure 3.
Aromatase inhibition in the dorsal dentate gyrus blocks the anxiolytic- and antidepressant-like effects of testosterone replacement. (3A,B) When infused with saline (GDX+T+SAL), gonadectomized rats receiving testosterone replacement spent more time in the center of an open field than gonadectomized rats receiving a placebo pellet and infused with saline (GDX+SAL), but not when infused with the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole (GDX+FAD+T). ** p < 0.01 vs. GDX+SAL, * p < 0.05 vs. GDX+FAD and GDX+FAD+T, Fisher’s PLSD post-hoc test. (3C) None of the treatments affected rats’ locomotion in the open field. (3D) Testosterone replacement increased sucrose preference of gonadectomized rats infused with saline, but not fadrozole. (3E) Representation of individual values depicted in panel 3C, highlighting the greater variability observed following treatment with the aromatase inhibitor fadrozole, compared to animals infused with saline. ** p < 0.01 vs. GDX+SAL, * p < 0.05 vs. GDX+FAD+T, † p = 0.0503 vs. GDX + FAD, Mann-Whitney post-hoc test.