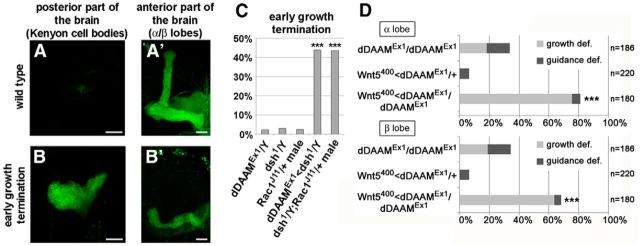
Figure 5.
The early axonal growth termination phenotype of dDAAM, dsh, and Rac1, and the genetic interaction between dDAAM and Wnt5. A–B′, A large fraction of the dDAAMEx1<dsh1/Y and dsh1/Y; Rac1J11/+ mutant combinations exhibit an early axonal growth termination phenotype. Unlike in wild-type (A, A′), the mutant MB axons fail to project anteriorly; instead, they form a ball-like structure in the posterior part of the brain (B, B′). FasII staining (green) was used to visualize the α/β and γ lobes. C, Quantification of the early growth termination phenotype in dDAAMEx1, dsh1, and Rac1J11/+ single and double mutant males. The double mutants exhibit this effect in a significantly higher proportion than the single mutants. D, Quantification of the MB axonal growth and guidance defects in dDAAMEx1and Wnt5400 mutant combinations. Note the strong dominant interaction between the two alleles. ***p ≤ 0.0001 (Fisher's exact test). Bars, 20 μm.